
Augmented Reality (AR) apps improve mobile apps by combining digital elements with the physical environment, allowing users to interact with virtual objects in real-world settings. These apps, built on AR technology, use cameras and sensors to overlay virtual elements onto real-world environments, creating unique user experiences. AR apps enable unprecedented interactivity by enriching reality instead of replacing it, making them a growing trend in app development.
In 2020, approximately 83.1 million consumers in the United States used augmented reality (AR) monthly, accounting for 15% of the population, according to a report by Statista. By 2023, this number had increased to around 90 million users. The AR gaming market is projected to reach nearly $11.5 billion by 2025.
Some of the most popular Augmented Reality apps include Google Lens, which provides real-time object recognition; IKEA Place, which enables users to visualize furniture in their homes; and the iconic Pokémon GO, which combines outdoor exploration with AR gameplay. These apps showcase the potential of immersive AR technology to create engaging and practical solutions across various domains, from entertainment to utility.
Key features of AR apps include markerless AR technology, which eliminates the need for physical markers, precise spatial mapping for accurate virtual object placement, and smooth integration with device hardware like cameras and motion sensors. These features ensure AR apps deliver smart and intuitive user experiences, making them a cornerstone of modern mobile apps.
AR apps are versatile in the diverse industries that utilize them, such as healthcare, education, eCommerce, and construction. For example, AR apps enhance classroom learning, facilitate online shopping with virtual shopping carts, and assist architects in visualizing building plans. This adaptability emphasizes AR's transformative role in industries that require innovative digital solutions.
The AR app development process involves defining requirements, selecting AR development frameworks like ARKit or ARCore, creating 3D assets, and rigorous testing. By combining technical expertise with creativity, developers ensure AR apps are functional, user-friendly, and compatible with various platforms. The result is a new generation of mobile apps that revolutionize user interaction and bridge the gap between technology and reality.
What is an Augmented Reality App?
An Augmented Reality (AR) app is a software application designed to overlay digital content, such as images, sounds, and other sensory enhancements, onto the real-world environment through a device such as a smartphone, tablet, or AR headset. AR apps blend the physical and digital worlds by utilizing the camera and sensors of these devices, , creating an interactive experience that enhances perception and interaction with the surroundings.

The primary aim of AR apps is to enrich real-world experiences with additional, contextually relevant information or entertainment. They are used in various fields, including gaming, education, healthcare, retail, and real estate. AR apps' benefits include improved user engagement, immersive learning experiences, enhanced visualization for design and planning, and interactive marketing opportunities.
AR apps function by combining hardware and software components. Devices equipped with cameras capture the user's environment, while sensors like GPS, gyroscopes, and accelerometers help determine the device's position and orientation. The AR app processes this data to identify and map physical spaces in real time.
AR apps use spatial awareness to overlay digital elements, such as 3D models, animations, or information onto the real-world view, ensuring they appear perfectly integrated. Advanced AR apps use technologies like SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) to achieve greater accuracy and realism.
The concept of AR dates back to the 1960s, when computer scientist Ivan Sutherland developed the first head-mounted display system, considered a precursor to modern AR devices. In the 1990s, Tom Caudell, a researcher at Boeing, coined the term "augmented reality."
AR technology gained mainstream attention in the 2000s with advancements in mobile computing and the release of ARToolKit, an open-source AR development kit. In 2016, AR experienced a massive surge in popularity with the release of the game Pokémon GO, demonstrating its potential for mass adoption.
In recent years, the global AR market has experienced rapid growth. According to a Grand View Research report, the market was valued at approximately $25 billion in 2021 and is projected to exceed $100 billion by 2030, driven by advancements in 5G, AI, and AR devices. Key sectors adopting AR include retail (for virtual try-ons), healthcare (for surgical simulations), and education (for immersive learning tools).
According to a report by Exploding Topics, over 1.4 billion AR-enabled devices were in use globally in 2023. Approximately 50% of consumers report using AR apps at least once. Social media platforms are a major driver, with AR filters on apps like Instagram and Snapchat reaching millions of users daily.
Retail AR adoption is also impressive. Forbes Council shows that 61% of consumers prefer shopping at stores offering AR experiences, and products featuring AR content have an average 40% higher conversion rate.
What are the Types of Augmented Reality Apps?
The different types of augmented reality (AR) apps are marker-based AR, markerless AR, and projection-based AR, among others. Each type uses distinct technology and methods to overlay virtual content onto the real world, serving various applications and industries. These types overlap with specific variations like location-based and superimposition-based AR, offering tailored solutions for unique use cases.
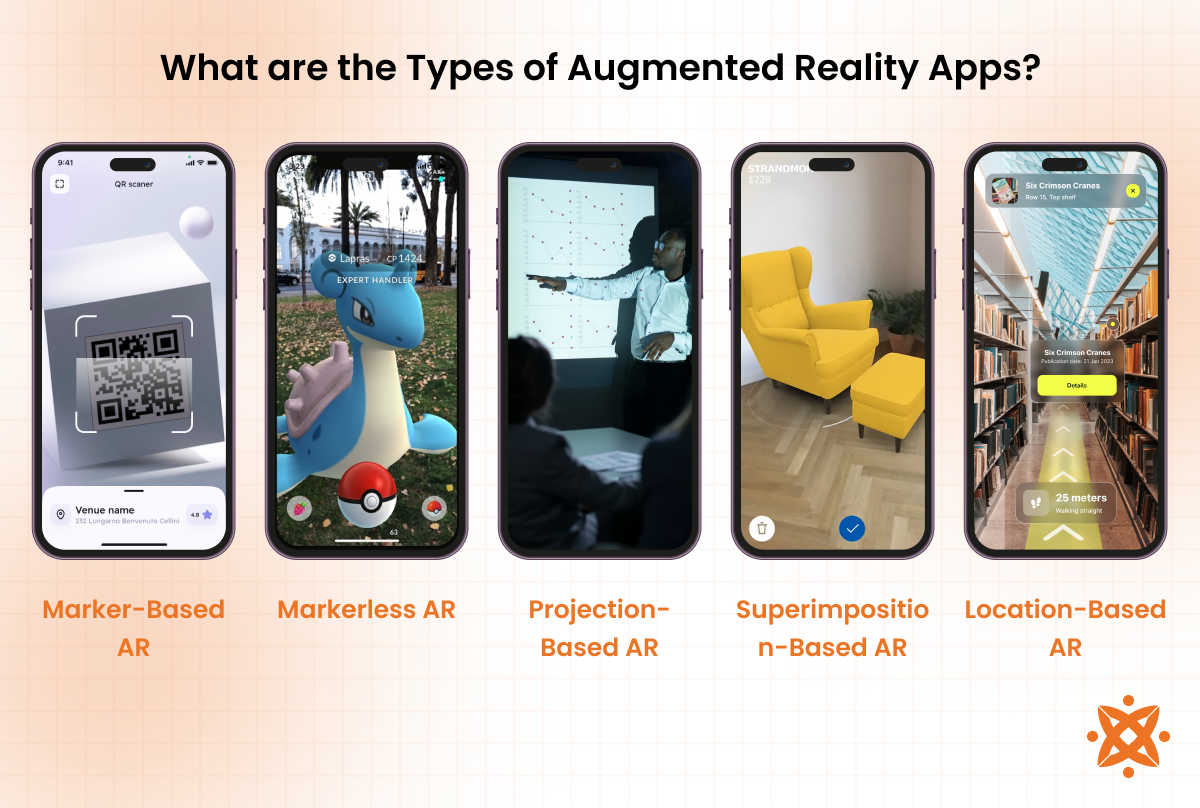
The different types of AR apps are as follows:
- Marker-Based AR: Marker-based AR uses visual cues, such as QR codes, images, or patterns, to trigger the display of virtual objects. The app scans the marker through the device's camera and places digital elements precisely on or around the marker. This type is used in interactive marketing, education, and gaming, allowing users to access engaging content by scanning objects or images. According to the study by Boonbrahm et al. 2020, titled “The Use of Marker-Based Augmented Reality in Space Measurement,” marker-based AR technology is utilized to develop an application that accurately measures the size and shape of rooms for facility management purposes.
- Markerless AR: Markerless AR, known as location-based or SLAM-based AR, does not rely on fixed markers. Instead, it uses the device's GPS, accelerometer, and gyroscope to map the environment and overlay digital content anywhere in real-world spaces. This type of AR is popular in apps like Pokémon GO, where users interact with virtual objects based on their geographic location. According to a study by Hasanah N et al. 2021, titled “Markerless Augmented Reality in Construction Engineering Utilizing Extreme Programming,” Android-based markerless AR application enhances learning in the construction field, specifically focusing on bridge materials for vocational students.
- Projection-Based AR: Projection-based AR involves projecting light or digital content onto real-world surfaces, allowing users to interact with the projection directly. This type does not require a screen or device for viewing, making it ideal for interactive displays, design visualization, and immersive experiences in museums or exhibitions. Lee J et al. 2015, in their study titled “Real-Time Projection-Based Augmented Reality System for Dynamic Objects in the Performing Arts,” demonstrated a real-time projection-based augmented reality system that accurately projects imagery onto the dynamic surfaces of actors' costumes during live performances, enriching the visual experience in the performing arts.
- Superimposition-Based AR: Superimposition-based AR replaces or enriches parts of the real-world view with augmented elements. For example, in healthcare, this type is used for surgical guidance by superimposing anatomical details over a patient's body. It provides detailed, context-aware information that helps improve precision and understanding. In their 2019 study, "Augmented Reality Types And Popular Use Cases," Filali et al. identified the IKEA Catalog app as an example of superimposition-based AR. This app lets users visualize virtual furniture in real-world environments, enhancing the shopping experience.
- Location-Based AR: A subset of markerless AR, location-based AR relies on GPS data to provide location-specific virtual content. This type is common in travel and navigation apps, offering features like virtual tours, interactive city guides, or historical reconstructions at specific landmarks.
What Are the Popular Examples of Augmented Reality Apps?
The most popular examples of augmented reality apps are Google Lens, IKEA Place, and Pokémon GO. These apps showcase the versatility of AR technology, offering solutions for productivity, retail, and entertainment. Each provides unique functionalities demonstrating how AR enhances user experiences across different domains.
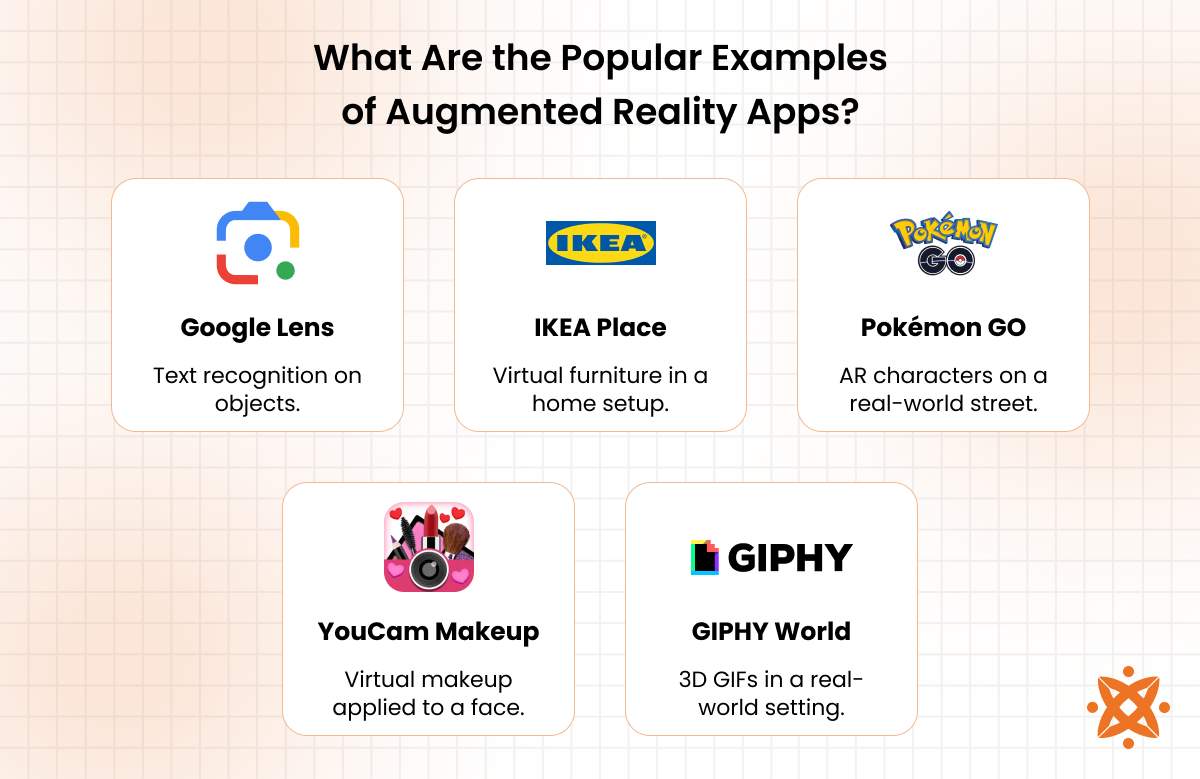
The most popular examples of AR apps are as follows:
1. Google Lens
Google Lens is an AI-powered AR app that turns your smartphone camera into a visual search tool. Users can identify items, translate text, or explore landmarks by pointing the camera at objects, texts, or places. The app uses AR to overlay contextual information directly onto the real-world view, making it highly intuitive and user-friendly.
The app's practical uses range from scanning QR codes to extracting contact details from business cards and shopping for items online by recognizing physical products. It enhances productivity and learning, making it a versatile tool for students, professionals, and everyday users.
2. IKEA Place
IKEA Place is an AR-based furniture visualization app that helps users design their living spaces. With this app, customers place true-to-scale 3D models of IKEA furniture in their rooms, ensuring the items fit spatially and stylistically. The app simplifies the decision-making process for shoppers by offering a preview before purchase.
This app is particularly valuable for interior designers and homeowners experimenting with layouts. By reducing uncertainty and enhancing customer satisfaction, IKEA Place improves the shopping experience and minimizes returns, demonstrating how AR creates practical solutions in retail.
3. Pokémon GO
Pokémon GO is a groundbreaking AR app that combines gaming with real-world exploration. Players use their smartphones to find and capture virtual Pokémon that appear in real-world locations, encouraging them to walk, explore, and engage with their environment. The game also features gym battles, trading, and events that foster community interaction.
The app's success lies in its blend of location-based AR and social elements, which make it entertaining and engaging. It revolutionized mobile gaming and showcased AR's potential for mass-market adoption, with millions of players around the globe embracing this interactive experience.
4. GIPHY World
GIPHY World is a creative AR app that allows users to insert 3D GIFs into their surroundings, creating playful and dynamic scenes. The app uses AR to place these animations in the real world, which users then capture and share with friends on social media.
Its fun, casual appeal makes it a favorite for social interactions and creative expression. Whether decorating a room with animated stickers or creating surreal visuals, GIPHY World highlights how AR is used for entertainment and personal creativity.
5. YouCam Makeup
YouCam Makeup is an advanced AR app designed for beauty enthusiasts. Using facial recognition and AR overlays, it allows users to try out makeup products virtually in real time. Users experiment with their new look without applying any products, from lipstick and eyeshadow to full makeup looks.
This app is useful for casual users and sweetens online shopping for beauty retailers. Personalized recommendations and virtual try-ons help shoppers make confident purchasing decisions, reduce returns, and increase engagement with beauty brands.
6. Augment
Augment is an AR app tailored for businesses to showcase 3D models of products in real-world settings. Whether for retail, architecture, or manufacturing, this app enables customers and clients to visualize items in their intended environments, facilitating decision-making and presentations.
Augment's focus on productivity supports collaboration and enhances the customer experience. It's particularly valuable for industries requiring precise visualization, making it a powerful tool for professionals and marketers aiming to demonstrate their ideas effectively.
7. Houzz
Houzz exploits AR to alter the home improvement and interior design experience. Its "View in My Room" feature enables users to place 3D models of furniture, decor and lighting into their spaces, allowing them to visualize and plan renovations or redecorations with confidence.
This app is ideal for homeowners and professionals, offering inspiration and practicality. By providing an immersive shopping and design experience, Houzz bridges the gap between imagination and reality, making home improvement more accessible and enjoyable.
8. AR Ruler
AR Ruler turns your smartphone into a virtual measuring tool. Using AR to map surfaces and dimensions, users measure distances, angles, and areas with their device's camera, eliminating the need for physical tools.
This app is highly practical for professionals in construction, architecture, and DIY enthusiasts. It simplifies tasks like estimating room dimensions or planning layouts, saving time and effort while ensuring precision.
9. Pokémon GO
Pokémon GO exemplifies the fusion of AR and location-based gaming. Players interact with virtual Pokémon scattered across real-world locations, encouraging physical activity and exploration. Social features like battles and events add a communal element, making the app a global phenomenon.
Its innovative gameplay demonstrates AR's ability to create immersive and engaging experiences. The success of Pokémon GO paved the way for other AR apps in gaming and beyond, proving the technology's broad appeal.
10. Quiver - 3D Coloring App
Quiver combines traditional coloring with AR to create an interactive experience. Users start by coloring printed pages and then use the app to bring their creations to life as animated 3D models. These models retain the user's unique coloring, making the experience highly personalized.
Quiver is perfect for children and educators, as it adds a layer of fun to learning and creativity. It showcases how AR engages young minds, encouraging creativity while blending digital and physical activities.
What are the Features of an AR App?
The main features of augmented reality (AR) apps are real-time interaction, spatial awareness, and immersive content integration. These features combine to create engaging and flawless experiences by blending the physical and digital worlds. AR apps ensure users interact naturally and intuitively with augmented elements.
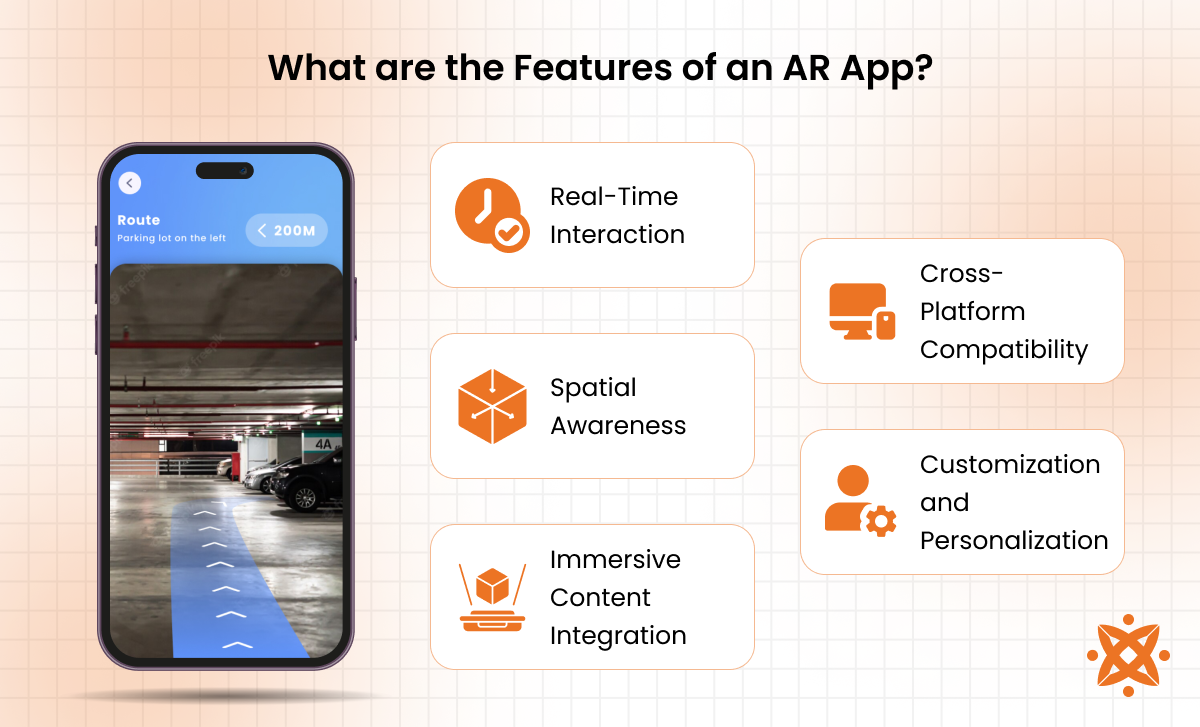
The main features of AR apps are as follows:
- Real-Time Interaction: Real-time interaction allows AR apps to respond instantly to user inputs and environmental changes. These apps process data and render virtual elements dynamically by utilizing device sensors and cameras. Real-time interaction ensures that AR experiences are smooth and engaging, whether users are playing games, exploring educational content, or visualizing designs.
- Spatial Awareness: Spatial awareness enables AR apps to understand and map the physical environment. AR apps use technologies like SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) to detect surfaces, measure distances, and determine object positions. This capability is necessary for placing virtual objects accurately and maintaining their stability as users move their devices.
- Immersive Content Integration: Immersive content integration overlaps high-quality 3D models, animations, and interactive elements into the real-world view. This feature ensures that digital content appears natural and engaging, improving user experiences. For example, it lets users preview home furniture or interact with virtual game characters.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Cross-platform compatibility ensures AR apps function perfectly on various devices and operating systems. This feature broadens the app's reach and usability by supporting iOS, Android, and AR-specific hardware like headsets, making AR experiences accessible to diverse audiences.
- Customization and Personalization: Customization and personalization allow AR apps to adapt to individual user preferences. Features like user-specific recommendations, adjustable AR settings, and personalized content enhance engagement by creating unique experiences for each user.
What are the Applications for Augmented Reality Apps?
The different applications for augmented reality (AR) apps are in industries such as education, healthcare, eCommerce, and entertainment. AR apps improve user experiences by providing interactive, immersive, and practical solutions customized to the needs of each sector.
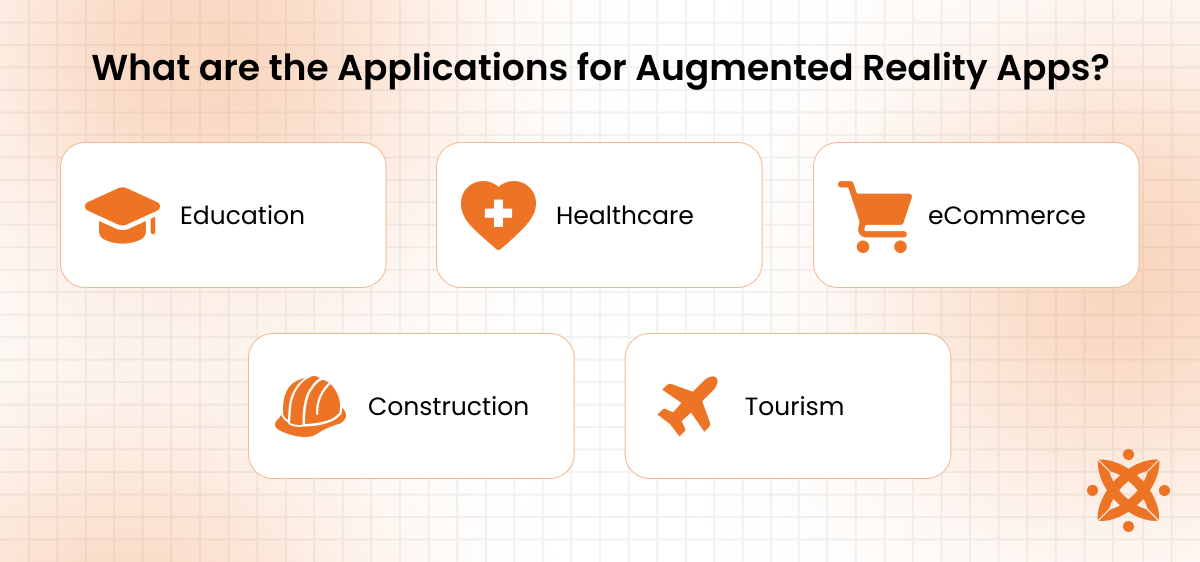
The different applications for AR apps are as follows:
- Automotive: AR is used in the automotive industry for driver assistance and training. AR heads-up displays provide real-time navigation, hazard warnings, and speed information directly on the windshield. AR is utilized in virtual car showrooms, allowing users to explore and customize vehicles before purchasing.
- Education: AR changes learning by creating interactive and engaging educational experiences. It brings concepts to life, such as visualizing 3D models of anatomy or historical landmarks. AR apps also enable virtual experiments and immersive storytelling, making education more accessible and effective for students, according to a study by Al-Ansi AM et al. 2023, titled “Analyzing augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) recent development in education.”
- Healthcare: In healthcare, AR is used for medical training, diagnostics, and surgical guidance. Surgeons visualize internal organs with AR overlays during procedures, while medical students benefit from realistic simulations. AR also aids patient education by providing detailed insights into treatments and conditions.
- Interior Design: AR apps in interior design allow users to visualize furniture, decor, and layouts in real-world spaces. By placing 3D models into their homes, users experiment with designs and make informed decisions, reducing uncertainty and improving satisfaction.
- Construction: AR enhances construction by offering real-time visualization of blueprints and project plans overlaid on the site, according to a study by Kodeboyina SM et a. 2016, titled “Low-Cost Augmented Reality Framework for Construction Applications.” Workers use AR to identify utilities, plan workflows, and ensure design alignment, increasing efficiency and reducing errors during construction.
- Landscaping: AR in landscaping helps homeowners and professionals visualize outdoor designs, such as garden layouts, patios, and pathways. Users experiment with aesthetics and functionality before implementation by overlaying virtual plants and structures onto real spaces.
- eCommerce: AR revolutionizes eCommerce by offering virtual try-ons and product visualization. Customers see how clothes, accessories, or furniture look before purchasing, boosting confidence and reducing returns. AR improves the online shopping experience by bridging the gap between physical and digital. The global AR in Retail market size is estimated to be worth $1853.7 million in 2021 and is forecast to a readjusted size of $6736.2 million by 2028 with a CAGR of 20.0% during the forecast period 2022-2028, according to PR Newswire. A 2015 study by Internet Retailer found that in-store clothing sales across every brand increased by only 1% during 2015, while online sales soared by 20% during that same year and reached $80 billion in the United States.
- Tourism: AR apps in tourism provide interactive guides and virtual tours. Users explore historical landmarks with AR overlays that share detailed information or visualize how sites looked in the past, making travel more engaging and informative.
- Fitness: AR enhances fitness experiences through interactive apps that gamify workouts or provide real-time form corrections. AR fitness games and trainers make exercising more engaging, motivating users to stay active and reach their goals.
- Social Media: AR is widely used in social media for filters, effects, and interactive content. Platforms like Instagram and Snapchat let users apply AR overlays to photos and videos, creating engaging and shareable experiences that drive user engagement.
- Entertainment: AR promotes entertainment by blending virtual and real-world elements. Popular applications include AR-based gaming, Pokémon GO, and immersive storytelling experiences. AR brings a new level of interactivity to media and live performances.
- Astronomy: AR apps for astronomy help users explore the night sky by identifying stars, planets, and constellations in real-time. With AR overlays, users learn about celestial objects, making stargazing a more educational and enjoyable experience.
- Beauty: AR apps enable virtual try-ons for makeup and hairstyles in the beauty industry. Users experiment with products in real-time, enhancing the shopping experience while helping brands connect innovatively with their audience.
How to Develop and Design Augmented Reality Apps for Android and iPhone?
To develop and design augmented reality (AR) apps for Android and iPhone, developers follow a structured process that includes planning, selecting the right AR frameworks, and implementing advanced AR features. Augmented Reality development framework ensures that apps are optimized for platform-specific capabilities while maintaining cross-platform support for broader usability.
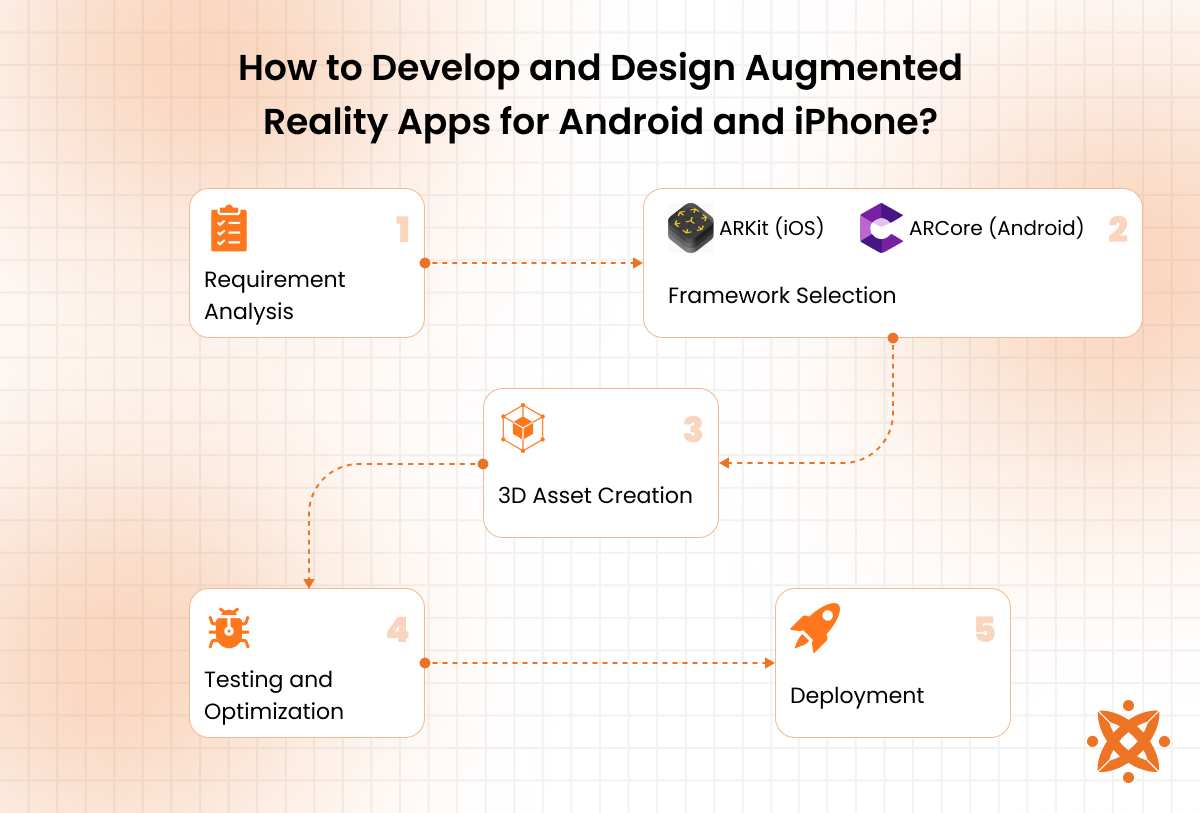
To develop and design mobile AR apps for Android and iPhone, the following steps are employed:
Android Augmented Reality App Design and Development Process
Developing AR apps for Android involves platform-specific tools and frameworks like ARCore. The process focuses on creating interactive experiences through markerless AR technology, using 3D modeling tools, and optimizing performance for a wide range of Android devices.
The Android Augmented Reality app design and development process involves the following steps:
- Requirement Analysis and Planning: The first step in developing an AR app for Android involves defining its purpose, target audience, and features. Developers also decide on the appropriate AR development framework, such as ARCore, to support markerless AR and ensure the app aligns with user expectations and industry standards.
- Designing the User Interface (UI): The UI is created using Android Studio, focusing on intuitive and visually appealing layouts. It must also allow smooth interaction with AR content, ensuring users easily engage with virtual elements in real-world settings.
- Implementing AR Features: In this step, developers integrate ARCore to enable markerless AR functionality, such as environment tracking and object placement. They also use 3D modeling tools like Unity or Blender to design realistic virtual objects, ensuring immersive experiences.
- Development and Integration: The app's functionality is developed using Java or Kotlin, including AR-specific features such as spatial mapping and gesture recognition. Developers ensure smooth integration of virtual objects with the physical environment, enhancing user engagement.
- Testing and Optimization: The app is tested on multiple Android devices to ensure compatibility and performance. Developers identify and fix bugs, optimize rendering speeds, and ensure the app provides consistent experiences across different hardware configurations.
- Deployment: The finalized app is published on the Google Play Store. Developers follow Android's guidelines for AR apps to ensure compliance and usability while providing updates based on user feedback.
iPhone Augmented Reality App Design and Development Process
Developing AR apps for iPhone involves utilizing Apple's ARKit and advanced iOS-specific tools like Xcode and Swift. The process emphasizes utilizing iPhone's hardware, such as LiDAR, and creating flawless AR experiences optimized for iOS.
The iPhone Augmented Reality app design and development process involves the following steps:
- Requirement Analysis and Planning: This step involves defining the app's goals and identifying features that align with user needs. ARKit is the primary framework, offering robust markerless AR technology, motion tracking, and environmental understanding specific to iOS devices.
- Designing the User Interface (UI): Developers create user-friendly interfaces using Xcode and SwiftUI, focusing on enhancing interaction with AR content. The UI must be intuitive, ensuring users navigate the app and interact with virtual elements effortlessly.
- Implementing AR Features: ARKit is integrated to enable advanced AR capabilities, such as object detection and plane recognition. Developers use 3D Augmented Reality modeling tools like Maya or Blender to create high-quality digital assets that align perfectly with the real-world environment.
- Development and Integration: Developers build the app's core functionality using Swift or Objective-C, which includes features like object manipulation and interactive animations. Special attention is given to utilizing iPhone-specific hardware, such as LiDAR, for advanced depth sensing and precision.
- Testing and Optimization: The app is rigorously tested on various iOS devices to ensure compatibility, performance, and stability. Developers optimize the app for features like ARKit's advanced APIs, ensuring smooth operation, minimal resource consumption, and AR content creation.
- Deployment: Once finalized, the app is submitted to the Apple App Store. Developers ensure compliance with Apple's strict guidelines for AR apps and provide ongoing updates to improve functionality and user experience.
What is the Cost of Developing Augmented Reality Apps?
The cost of developing augmented reality (AR) apps ranges from £10,000 - £30,000, depending on the app's complexity and features. Simple AR applications, such as basic marker-based apps, cost between £5,000 and £10,000, while complex and feature-rich apps, such as those with advanced markerless AR technology, 3D modeling, or integration with IoT devices, range from £100,000 to £150,000.
Several factors influence the cost of AR app development. These include the app's complexity, AR technology (e.g., marker-based, markerless, or projection-based), and the development platform (Android, iOS, or cross-platform). Custom 3D modeling, premium AR development frameworks like ARKit or ARCore, and hardware integration, such as LiDAR or AR headsets, also play a significant role.
The level of interactivity, content personalization, and ongoing maintenance or updates further impact the overall cost of developing augmented reality (AR) apps. Businesses should carefully evaluate their requirements and budget constraints to plan effectively for AR app development.
What are the Challenges in AR App Development?
The common challenges in AR app development are hardware limitations, AR content creation complexity, and ensuring excellent user experiences across platforms. These challenges require innovative solutions and careful planning to deliver high-quality and reliable applications.
Hardware limitations pose a significant challenge, as AR apps rely on advanced sensors, cameras, and processors to function effectively. Not all devices are equipped to handle AR's demands, which impact app performance and accessibility. Creating realistic and engaging AR content is complex, requiring expertise in 3D modeling, animation, and specialized use of AR development frameworks.
Ensuring a perfectly integrated user experience across platforms adds another layer of difficulty. Developers must address differences between Android and iOS ecosystems, integrate markerless AR technologies, and optimize apps for varying screen sizes and hardware capabilities. These challenges emphasize the need for skilled developers and robust testing to deliver immersive and consistent AR experiences.
What is the Difference Between an Augmented Reality App and a Virtual Reality App?
The main difference between an augmented reality app and a virtual reality app is how they interact with the real world. Augmented reality (AR) apps overlay digital elements onto the physical environment, enriching real-world interactions. In contrast, virtual reality (VR) apps fully immerse users in a simulated environment, blocking out the real world entirely.
AR apps, such as AR games or interior design tools, use cameras and sensors to blend virtual objects with real-world settings. Virtual Reality apps, on the other hand, require specialized hardware, such as VR headsets, to create 360-degree environments for gaming, simulations, or training. While AR improves reality, VR replaces it, offering entirely distinct use cases and user experiences.
How to Choose an Augmented Reality App Development Company
To choose an Augmented Reality App development company, prioritize their expertise in AR technologies, such as ARKit, ARCore, and markerless AR. Verify their portfolio for successful projects that align with your industry and app requirements, ensuring they have a proven track record of delivering quality AR apps.
Consider their ability to provide cross-platform support, handle complex 3D modeling tasks, and offer post-development maintenance services. Other evaluation factors include the company's reputation, client reviews, communication process, and understanding of your specific business needs. A well-rounded approach ensures you partner with a company that delivers innovative and reliable AR solutions.
What Are the Qualifications for an Augmented Reality App Developer?
The main qualification for an augmented reality app developer is proficiency in AR development frameworks like ARKit, ARCore, or Vuforia. These frameworks form the foundation of AR app development, enabling developers to integrate features like object recognition, motion tracking, and 3D rendering.
Depending on the platform, developers must also have a strong grasp of programming languages such as Swift, Kotlin, C#, or UnityScript. Skills in 3D modeling and design tools like Blender or Maya are necessary for creating realistic virtual assets. Knowledge of user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design ensures great interactions with AR content.
Strong problem-solving abilities, attention to detail, and experience with cross-platform development are also paramount for addressing the unique challenges of AR app development. Collectively, these qualifications enable developers to create engaging and functional AR applications.
Never Miss an Update From Us!
Sign up now and get notified when we publish a new article!
Dhaval Sarvaiya
Co-Founder
Hey there. I am Dhaval Sarvaiya, one of the Founders of Intelivita. Intelivita is a mobile app development company that helps companies achieve the goal of Digital Transformation. I help Enterprises and Startups overcome their Digital Transformation and mobile app development challenges with the might of on-demand solutions powered by cutting-edge technology.
