.png&w=1920&q=75)
Augmented Reality (AR) is a state-of-the-art technology that integrates virtual elements into the real world, enhancing users' experiences of their surroundings. AR bridges the gap between the digital and physical worlds by superimposing real-time digital overlays onto a live view of the physical environment.
Unlike virtual reality, which creates entirely simulated environments, AR improves and interacts with the real world, offering users an enriched and more engaging experience. According to Statista's report “AR & VR - United Kingdom,” AR user penetration is 81% in 2024 and is expected to rise to 83.3% by 2029, with younger demographics leading in engagement.
The benefits of augmented reality include improvements in user experience and operational efficiency. AR enables immersive experiences where users interact with digital objects in real-world environments. This makes processes like training, education, and shopping more interactive and enjoyable. Businesses also benefit from AR by using it to enrich marketing strategies and improve customer engagement.
Augmented reality technology involves using AR applications that rely on cameras, sensors, and software to detect and map the physical environment. Once the environment is understood, AR systems overlay digital content in the real world.
Augmented reality development platforms build these applications, providing tools and frameworks for creating interactive and immersive experiences.
Advanced technologies, such as head-mounted AR displays or smartphone screens, are commonly used to deliver these experiences. Through tracking devices and location-based services, AR offers real-time, context-sensitive information, turning ordinary environments into interactive and dynamic spaces.
AR technology is used in industries such as retail, where customers try on clothes or visualise products in their homes before purchasing. In education, AR brings learning materials to life through interactive simulations.
In the healthcare sector, AR assists with surgery planning and medical training. Augmented reality in real-world environments is also changing entertainment, with games like Pokémon GO leveraging AR to blend virtual gameplay with physical locations. According to a study by Byte Plus titled "Impacts of AR & VR on the Gaming Industry," AR technology delivers 40% faster rendering times and reduces development complexity by 50%.
The difference between augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) lies in their approach to user immersion. While AR overlays digital content in the real world, creating an interactive experience without fully immersing users in a virtual space, VR creates entirely simulated environments that replace the real world.
Both technologies offer unique experiences and are used for different purposes, but AR's ability to improve real-world environments with digital information makes it more accessible and versatile in everyday life.
- What is AR (Augmented Reality)?
- What are the Examples of Augmented Reality?
- What are the Benefits of Augmented Reality?
- How Does Augmented Reality Technology Work?
- What are the Use Cases of Augmented Reality Technology?
- What is the Difference Between Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality?
- What is the Future of Augmented Reality Technology?
- What Does the Augmented Reality Development Process Involve?
What is AR (Augmented Reality)?
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital content, such as images, sounds, or other data, onto the real-world environment through devices such as smartphones, tablets, AR glasses, or headsets.

Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which immerses users in a completely digital environment, AR improves the real world by adding virtual elements, allowing users to interact with both simultaneously. This interactive and immersive experience bridges the gap between the physical and digital worlds, offering new possibilities across various industries.
Augmented Reality (AR) is used across numerous fields to improve user experience and provide innovative solutions. In retail, AR enables virtual try-ons for clothing, glasses, and makeup. In education, AR offers interactive learning tools that bring subjects like history or science to life.
Healthcare professionals use AR for advanced diagnostics and surgical procedures, while architects and engineers employ it for 3D modelling and project visualisation.
AR is prevalent in entertainment and gaming, with applications like Pokémon GO showcasing its potential to merge gaming with real-world environments. Marketing and advertising campaigns also leverage AR to create engaging, interactive content for consumers.
The concept of augmented reality dates back to the 1960s, when computer scientist Ivan Sutherland developed the first head-mounted display system, considered a precursor to AR technology.
In the 1990s, Tom Caudell, while working at Boeing, coined the term. The technology gained traction in the 2000s with the advent of smartphones, which provided a portable platform for AR applications.
Early examples include AR markers and simple overlays. By the 2010s, breakthroughs in computer vision, GPS, and hardware enabled more sophisticated AR experiences, such as Snapchat filters and AR-enhanced mobile games.
In the UK, AR adoption is steadily growing, driven by industries such as retail, healthcare, and entertainment. User penetration is about 81% in 2024 and is expected to reach 83.3% by 2029, with younger demographics being the most engaged, according to Statista's report titled “AR & VR - United Kingdom.”
In the United Kingdom, revenue in the AR & VR market is around US$1,458.0m in 2024. Revenue is expected to show an annual growth rate (CAGR 2024-2029) of 9.27%, resulting in a projected market volume of US$2,271.0m by 2029.
What is an Augmented Reality Device?
An augmented reality (AR) device is any hardware designed to integrate digital content into the real world by superimposing it onto the user's physical surroundings.
These devices use a combination of cameras, sensors, displays, and processors to track the environment and align virtual objects with it in real time.
AR devices range from handheld tools like smartphones and tablets to wearable technology such as AR glasses and headsets, enabling immersive and interactive experiences.
Examples of AR devices include smartphones equipped with AR features, such as the iPhone and Android devices, which use ARKit and ARCore, respectively.
Wearable devices like the Microsoft HoloLens and Magic Leap glasses provide hands-free AR experiences for industrial and creative applications.
Other examples include AR headsets used in gaming, such as the Nreal Light glasses, and specialised devices like the Vuzix Blade, which offers AR features for enterprise solutions.
What are the Examples of Augmented Reality?
Examples of augmented reality are applications like Snapchat filters, Pokémon GO, IKEA Place, Google Lens, and AR-based virtual try-on tools. Each demonstrates the versatility of AR across different domains.

The examples of augmented reality are as follows:
- Snapchat Filters: Snapchat filters are AR features that add virtual effects to users' faces or surroundings in real time through the Snapchat app. They are widely used for entertainment and social media engagement.
- Pokémon GO: Pokémon GO is an AR mobile game that overlays virtual Pokémon characters onto the real world, encouraging players to explore their environment while capturing characters. It has revolutionised gaming by merging physical activity with digital interaction.
- IKEA Place: IKEA Place is an app that allows users to visualise how furniture would look and fit in their home spaces. By using AR, it simplifies the shopping experience and helps consumers make informed decisions.
- Google Lens: Google Lens uses AR to identify objects, translate text, and provide information about surroundings through a smartphone camera, enhancing learning and productivity.
- Virtual Try-On Tools: Virtual try-on tools are used in retail, and these tools enable customers to see how clothing, makeup, or eyewear looks on them without physically trying the items. They are popular in e-commerce for improving customer satisfaction and reducing returns.
What are the Benefits of Augmented Reality?
The main benefits of augmented reality include enhanced user engagement, improved decision-making, and increased operational efficiency. These advantages showcase AR's transformative potential across industries.
The benefits of augmented reality are as follows:
- Enhanced User Engagement: AR creates immersive and interactive experiences that more effectively capture users' attention. In entertainment, for example, AR applications like gaming or social media filters keep users engaged by blending digital elements with their real-world environment. AR experiences boost brand recall by up to 70%, which is higher than traditional digital advertisements. According to a study by Noomo Agency, AR content is more likely to be shared across social networks, with some campaigns seeing share rates increase by more than 50%.
- Improved Decision-Making: AR provides realistic visualisations and contextual information, aiding consumers and professionals in making informed decisions. Industries like retail and real estate benefit greatly, with tools such as virtual try-ons or property walkthroughs helping customers visualise products or spaces. Increased conversion rates: According to a study by Noomo Agency, AR increases conversion rates by 20-40%.
- Increased Operational Efficiency: AR integrates processes by providing real-time data and visual guidance. In healthcare, it assists surgeons with accurate overlays during procedures, while in manufacturing, it improves productivity by guiding workers through complex tasks using AR overlays.
How Does Augmented Reality Technology Work?
Augmented reality technology works by integrating digital content into the user's real-world environment in real time through advanced hardware and software. This is achieved by using a combination of cameras, sensors, and processors to analyse the surroundings and superimpose virtual elements accordingly.
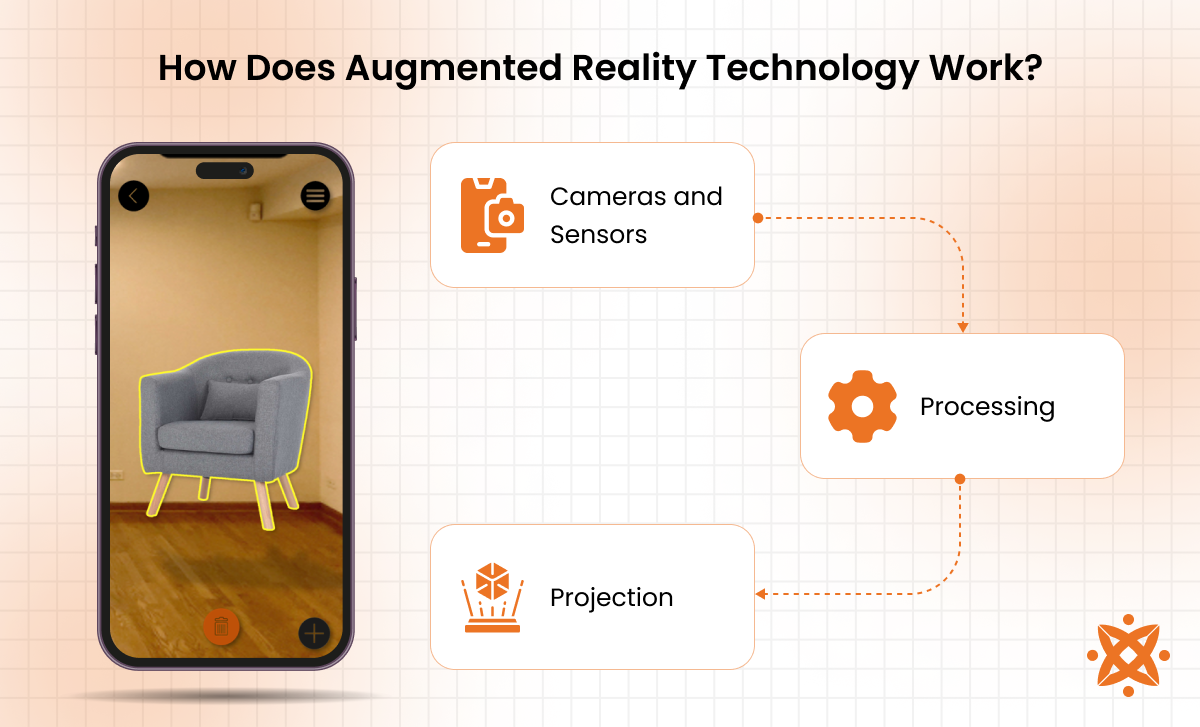
AR devices first use cameras and sensors to capture the user's environment. The captured data is processed by AR software, which uses computer vision technology to identify physical objects, surfaces, and spatial dimensions. Once the environment is mapped, digital content, such as 3D models or animations, is aligned and overlaid onto the physical world.
Real-time updates ensure that virtual elements remain in sync with the user's movements and perspective. For instance, AR apps like IKEA Place use this technology to allow users to visualise furniture in their homes with accurate scaling and positioning.
AR relies on technologies such as GPS, motion tracking, and machine learning to deliver smart, interactive experiences across various industries.
What are the Use Cases of Augmented Reality Technology?
The use cases of augmented reality technology include Retail Products, Metaverse, Marketing and Digital Advertising Campaigns.
From entertainment and gaming to healthcare and education, AR is transforming how businesses connect with audiences and create innovative, engaging environments.
The use cases of augmented reality technology are as follows:
- Retail Products
- Metaverse
- Marketing and Digital Advertising Campaigns
- Entertainment and Gaming
- Commercial Product Line Design and Manufacturing
- Healthcare
- Education
- Construction
- Sports
Retail Products
The retail products use case involves utilising AR to improve the shopping experience. AR allows customers to try out products virtually, such as clothing or accessories, without physically interacting with them.
For example, beauty apps provide virtual makeup try-ons, and furniture retailers offer virtual home product placement.
According to a study by Celestin M et al. 2024, titled "Exploring the Impact of AR and VR on Enhancing Customer Experiences and Driving Sales in Retail," retailers utilising AR/VR reported a 25% reduction in product returns and a 20% increase in conversion rates.
Metaverse
The metaverse incorporates AR to create immersive digital environments where users interact with virtual objects and each other. AR bridges the real and digital worlds, enabling applications in virtual meetings, virtual real estate tours, and collaborative spaces.
According to Statista, the metaverse AR and VR hardware market reached a value of US$1.6bn in 2024. This market segment is expected to display an annual growth rate (CAGR 2024-2030) of 12.77%, resulting in a projected market volume of US$3.3bn by 2030.
Marketing and Digital Advertising Campaigns
Augmented Reality (AR) has revolutionised marketing and advertising by enabling brands to create immersive, interactive campaigns that captivate and engage audiences. By using AR filters on popular platforms like Instagram and Snapchat, brands allow consumers to virtually try products, enhancing the overall experience and encouraging social sharing. This not only boosts customer engagement but also drives sales.
According to a study by Du Z, Liu J, Wang T. et al. (2022) titled "Augmented Reality Marketing: A Systematic Literature Review and an Agenda for Future Inquiry," customers who used AR to sample products spent 50% more time at the sampling fixture and were 19.8% more likely to make a purchase. This highlights the power of AR in enhancing customer interaction and fostering deeper connections with brands.
Entertainment and Gaming
In the entertainment and gaming industries, AR improves user experiences by blending digital content with the real world. Games like Pokémon GO and AR-based escape rooms use this technology to create immersive and interactive environments, allowing players to engage with both virtual and physical worlds simultaneously.
According to a study by Byte Plus in "Impacts of AR & VR on the Gaming Industry," AR technology delivers 40% faster rendering times, reduces development complexity by 50%, and offers improved user interaction models, further upgrading the gaming experience and driving innovation in the industry.
Commercial Product Line Design and Manufacturing
AR assists in the design and manufacturing of commercial products by providing visual prototypes and overlays. This reduces errors and speeds up production processes. For instance, AR simulates how machinery parts fit together, improving efficiency.
Healthcare
Healthcare applications of AR include surgical guidance, vein visualisation, and training simulations. Surgeons use AR to project images of internal organs onto patients, improving precision during procedures. AR-based medical training also improves medical professionals' learning.
Education
AR revolutionises education by providing interactive and immersive learning experiences. AR apps bring historical events to life or simulate complex scientific processes, making subjects more engaging and easier to understand.
Construction
AR is used in construction for planning, visualisation, and on-site guidance. Architects and engineers overlay building models onto construction sites, ensuring accuracy and streamlining workflows.
Sports
AR enriches sports broadcasting and training by providing real-time data overlays. For instance, AR systems display player statistics or simulate game scenarios, improving fan engagement and athlete performance.
What is the Difference Between Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality?
The main difference between augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) is that AR overlays digital content in the real world, while VR creates a completely immersive digital environment that disconnects users from the physical world.

In AR, users continue to interact with their actual surroundings, with virtual objects or information enhancing their real-world experience. On the other hand, VR immerses users in a fully virtual environment, requiring a headset to block out external stimuli.
While augmented reality improves the real world by adding interactive elements, Virtual Reality replaces it with a completely fabricated space. AR is used in applications like navigation, gaming, and retail, while VR is more commonly used in simulations, training, and immersive gaming experiences.
What are the Differences Between Augmented Reality and Mixed Reality?
The main difference between augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR) is that AR overlays digital content in the real world, while MR combines both virtual and real elements to interact in real time.
In AR, digital objects are placed in the user's environment but do not interact with it. For instance, AR displays virtual objects like a 3D model of a car in a physical space, but the virtual object remains static and does not respond to changes in the environment. In contrast, MR allows for more dynamic interaction, where digital elements not only appear in the real world but also interact with physical objects in real time.
While AR is primarily used to enhance experiences like navigation, gaming, and retail, MR is more advanced and is used for applications requiring immersive, interactive simulations, such as design, education, and professional training.
For example, in MR, a virtual character walks around a real-world table, responds to physical obstacles, or manipulates real-world objects.
What is the Future of Augmented Reality Technology?
The future of augmented reality technology is poised for significant growth and integration across various industries, with advancements in hardware, software, and user experience.
Key developments will include more effective integration into everyday life, improved by lighter, more powerful AR glasses and devices.
As AR technology continues to mature, we expect increased adoption in fields such as healthcare, retail, education, and entertainment, leading to more immersive and interactive user experiences.
In the coming years, AR will transform how people shop, learn, and interact with digital content. In retail, for example, AR will enable more personalised shopping experiences, where customers try products virtually before purchasing.
In education, AR will offer innovative ways to visualise complex concepts, improving learning outcomes through interactive simulations. The rise of the metaverse will see AR become a key component in creating virtual spaces that blend effortlessly with the real world.
As 5G networks expand, the speed and connectivity of AR applications will also improve, allowing for real-time, high-quality experiences.
Industries like healthcare will leverage AR for surgical precision, patient diagnostics, and remote consultations.
With the rapid development of AI and machine learning, AR will become more intelligent, offering context-aware experiences that adapt to users' needs. As these technologies evolve, AR is likely to become an important tool in daily life, enhancing how we work, socialise, and interact with the world around us.
Are There Augmented Reality Apps?
Yes, there are numerous augmented reality apps available across various platforms. These apps leverage AR technology to improve user experiences by overlaying digital content in the real world.
Common examples include apps like Pokémon GO, which allows players to catch virtual creatures in real-world locations, and IKEA Place, which enables users to visualise how furniture would look in their homes before making a purchase.
Other popular Augmented Reality apps include Snapchat and Instagram, which offer AR filters for photos and videos, and Google Lens, which helps users identify objects, translate text, and explore the world around them using their smartphone cameras. These apps demonstrate a diverse range of AR applications, from gaming and social media to shopping and productivity.
What Does the Augmented Reality Development Process Involve?
The augmented reality development process involves designing and creating digital experiences that blend virtual content with the real world. This process includes stages such as concept design, content creation, AR software development, and integration with hardware.
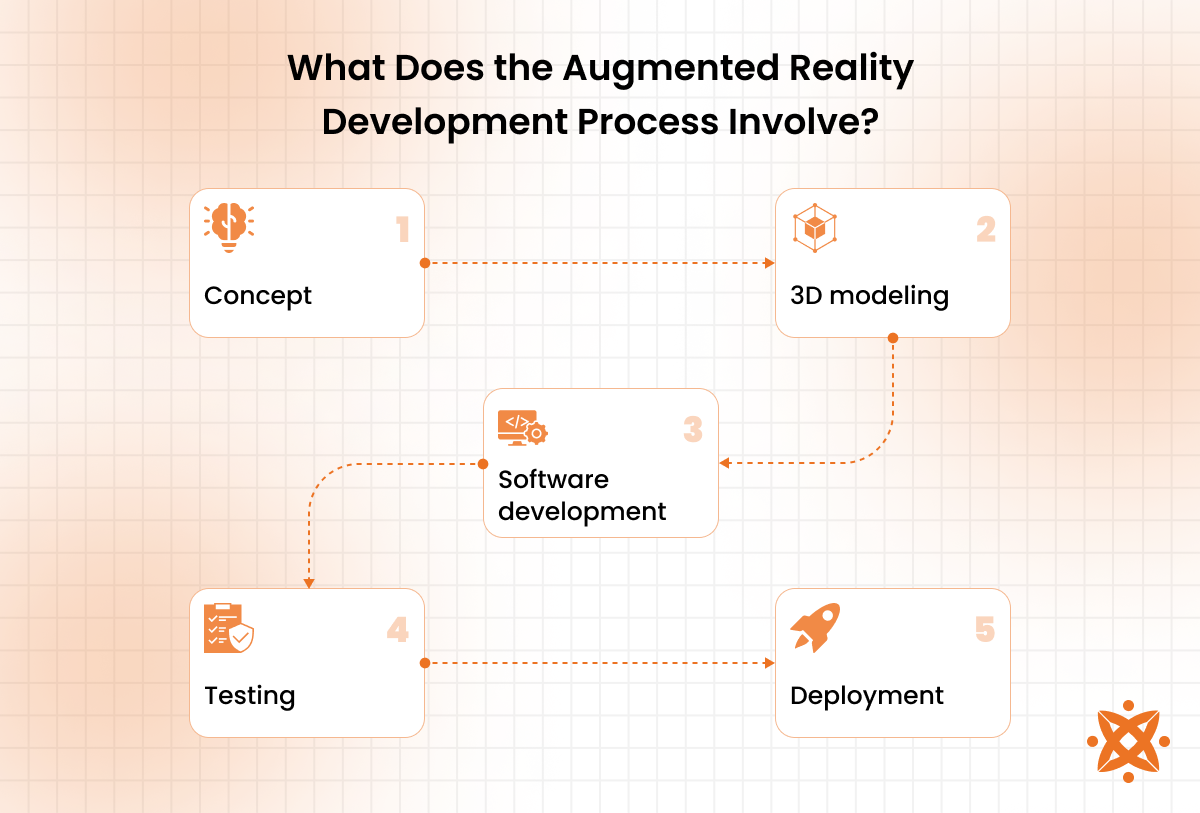
At the beginning of the augmented reality development process, developers and designers outline the concept and goals of the AR application, considering the target audience and the intended user experience.
Once the idea is clear, the next step involves creating 3D models, animations, and other digital content that will be overlaid onto the real world. This content must be optimised for AR interactions and performance.
The software development phase follows, where AR-specific platforms and tools (such as ARKit or ARCore) are used to build the application. During this phase, features like object recognition, tracking, and spatial mapping are integrated to allow the virtual elements to interact effortlessly with the physical environment.
Finally, the AR application is tested and refined to ensure smooth and intuitive functionality and user experience. This includes testing for issues like lag or tracking errors, ensuring compatibility across devices, and gathering user feedback for further improvement.
Once the app is fully developed, it is ready for deployment on platforms like iOS or Android, where users access it. The development process is iterative, with frequent updates and refinements to improve the app's performance and features based on user feedback and technological advancements.
Never Miss an Update From Us!
Sign up now and get notified when we publish a new article!
Oliver Baker
Co-Founder
Oliver Baker is a co-founder of Intelivita, a leading Web and Mobile App Development Company based in Leeds, UK. Oliver has been at the forefront of the business, expanding it globally and into new technologies including iOS and Android, AR, VR and Mobile Game applications. Oliver excels in Project Management, Leadership, Quality Assurance and Problem Solving and has qualifications with Prince2 and APM. He aims to develop his skills further through a shared interest with other leaders in the Software Markets and the Clients of Intelivita.
