
A React Native app is a cross-platform mobile application built using JavaScript or TypeScript, allowing a single codebase to run on both iOS and Android. It bridges JavaScript with native UI components to deliver high performance and native-like user experiences.
The best frameworks and tools for React Native app development include Expo, Redux, React Navigation, TypeScript, and CodePush. These tools support streamlined development, efficient state management, real-time updates, and fast deployment.
The main programming languages used in React Native development are JavaScript and TypeScript, with JSX used for UI components. Native modules also require Java, Kotlin, Objective-C, or Swift when integrating advanced platform-specific features.
To develop a React Native app, set up the development environment using Node.js and either Expo or React Native CLI, build UI components with JSX, integrate APIs or databases, test across devices, and deploy to the App Store or Google Play Store. This method speeds up mobile development while maintaining native app standards.
According to Statista, 32% of developers used React Native in 2024, making it the second most popular cross-platform framework worldwide. It also accounts for a growing share of the mobile app market, with increasing adoption by startups and enterprise teams for scalable cross-platform solutions.
A React Native app is a mobile application developed using the React Native framework, which allows you to write code in JavaScript and render it using native components on both Android and iOS devices.

Unlike a web or hybrid app, a React Native app delivers a native-like experience by leveraging the same building blocks used in traditional native app development, but with a shared codebase across platforms.
You would use a React Native app when you want to launch quickly across both platforms without building separate apps in Swift for iOS or Kotlin for Android. Use cases include e-commerce platforms, social media apps, live event apps, and on-demand services, where time-to-market, UI responsiveness, and app store deployment are important.
The architecture of a React Native app includes a JavaScript layer that communicates with native modules through a bridge. The app's UI is built using React components, while native modules handle performance-intensive features such as animations, navigation, and device access. You also integrate APIs, databases such as Firebase, and services using backend frameworks like Node.js or Django.
Examples of popular React Native apps include Facebook, Instagram, Bloomberg, and Discord. Each app uses React Native to deliver fast updates, reduce code duplication, and offer a consistent experience across Android and iOS.
React Native is an open-source framework that lets you build mobile apps using JavaScript and React, then run them as native applications on both iOS and Android platforms. Instead of writing separate code for each OS, you use a single codebase that translates into native components at runtime, preserving app performance and responsiveness.

React Native is completely free to use. It's maintained by Meta (formerly Facebook) and supported by a wide developer community, making it accessible for individuals, startups, and large enterprises alike.
The benefits of using React Native include reduced development time, shared logic between platforms, and access to native features through pre-built modules. You can also leverage hot reloading, extensive third-party libraries, and consistent UX/UI behaviour across devices.
React Native is best suited for apps that prioritise user interface, rapid iteration, and cross-platform deployment, like MVPs, e-commerce apps, social networks, event platforms, and mobile dashboards. It's less ideal for highly graphics-intensive games or apps requiring complex native APIs not yet supported by the framework.
Companies using React Native in production include Facebook, Instagram, Shopify, Skype, and Tesla. These firms rely on React Native app development to streamline code reuse, push updates faster, and scale features across platforms efficiently.
A React Native app works by combining the declarative UI logic of React with native mobile components, allowing you to build cross-platform applications using JavaScript. Unlike hybrid apps that rely on WebView, React Native renders actual native UI elements, resulting in a smoother, more integrated user experience on both iOS and Android.
The core of this process lies in the React Native bridge, which acts as a communication layer between JavaScript and native code. When you write components in JavaScript, they are interpreted and passed through this bridge to invoke native APIs, such as camera, GPS, or gesture controls, on the host device.
React Native's architecture ensures that UI updates, gestures, and animations are handled natively, while business logic runs in a separate JavaScript thread. This division enables your app to maintain app performance similar to that of a native app, without requiring separate codebases.
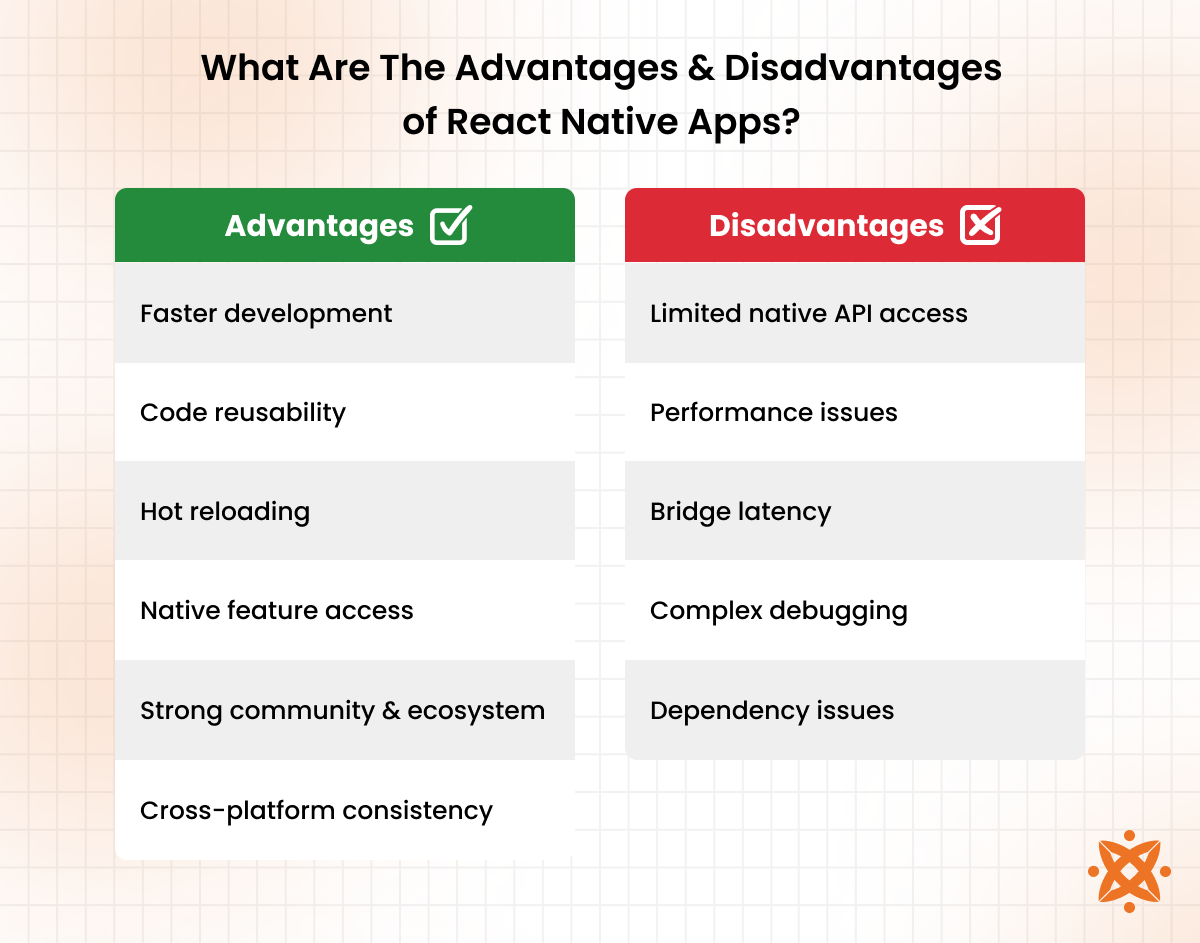
The benefits of React Native apps include faster development, code reuse, and consistent user experience across platforms. Since most of the codebase is shared between iOS and Android, you reduce both time and cost, which is especially useful when launching quickly or maintaining updates for both platforms simultaneously.
React Native also supports access to native device features through built-in modules or third-party libraries. This means your app interacts with the camera, location services, notifications, and more, just like a traditional native app. Additionally, tools like hot reloading and live debugging improve developer productivity by allowing real-time changes without restarting the app.
You also benefit from a large ecosystem and community. The framework integrates smoothly with popular databases like Firebase, testing tools, and design systems. This makes it easier to scale, test, and update your app while ensuring strong UX/UI performance across different devices.
The drawbacks of React Native apps include limited access to some advanced native APIs and occasional performance gaps for complex use cases. While the framework supports many common features, you may still need to write platform-specific code for things like advanced animations, background processing, or native integrations not yet covered by the React Native ecosystem.
The reliance on the bridge for communication between JavaScript and native modules introduces latency, particularly in applications with high-frequency data exchange or performance-critical tasks, such as gaming or video processing. Debugging is also more complex, as errors occur across both the JavaScript and native layers.
Additionally, dependency management becomes a challenge when third-party libraries aren't regularly maintained or compatible with the latest versions of React Native. This increases the effort required for updates and testing, particularly when supporting multiple OS versions.
The best frameworks and tools for React Native app development are those that enhance productivity, simplify UI design, and support full access to device capabilities. These tools help you write efficient, cross-platform code while maintaining native-level performance and user experience.

The best frameworks and tools for React Native development are explained below:
The following are frontend React Native app development frameworks:
The following are backend React Native app development frameworks:
The following are full-stack React Native app development frameworks that offer both frontend and backend capabilities in a unified setup:
The most commonly used databases for React Native app development include the following:
The most useful React Native CSS frameworks and UI libraries for designing responsive, consistent interfaces include:
The main programming languages used for React Native app development are JavaScriptand TypeScript, with Java, Kotlin, Objective-C, and Swift utilised for integrating native modules. These languages collectively enable you to build fast, maintainable, and scalable cross-platform apps while preserving native performance.
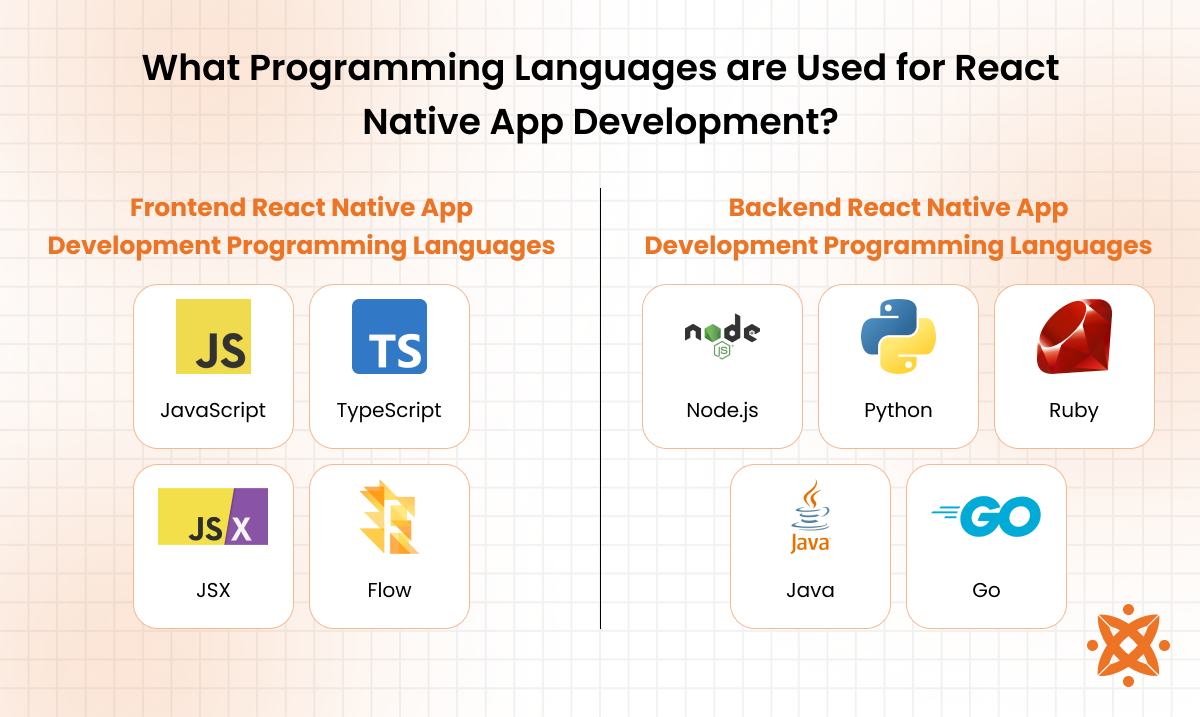
The programming languages used for react native app development are explained below:
The most used frontend programming languages for React Native app development include the following:
The most effective backend programming languages for React Native app development are explained below:
To make a React Native app, you start by installing Node.js, setting up the React Native CLI or Expo, and creating a project using JavaScript or TypeScript. From there, you build your UI with React components, integrate APIs and databases, test the app across devices, and deploy it to the App Store or Google Play Store.
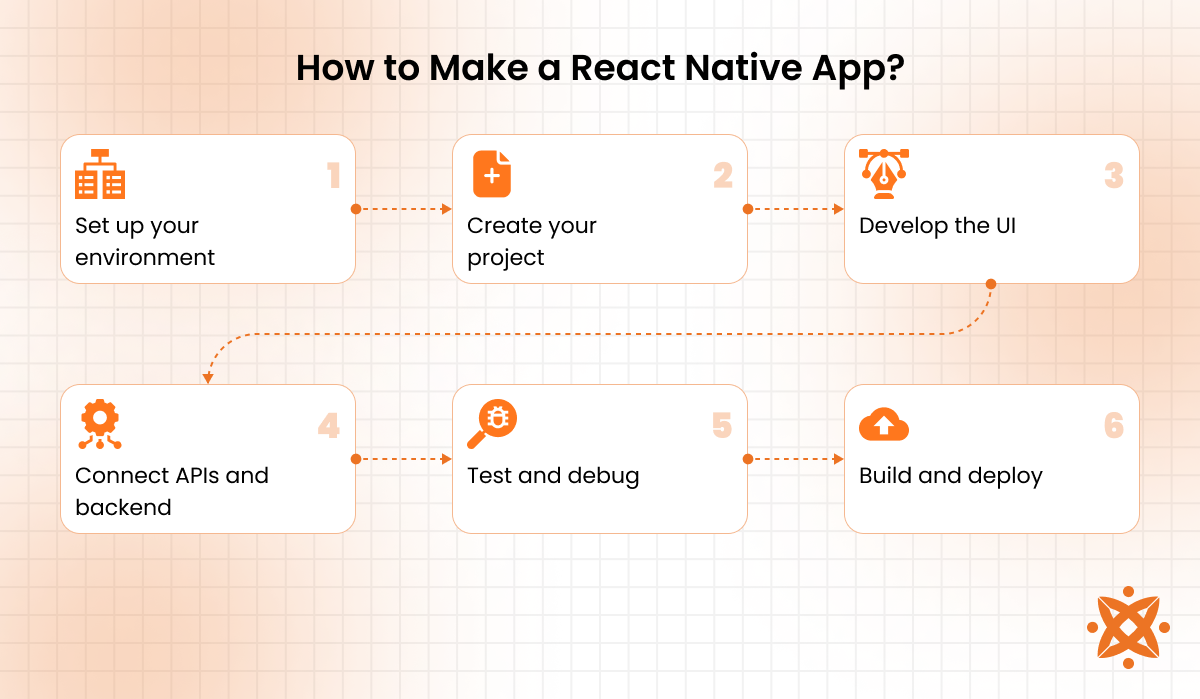
Here's how to make a React Native app, explained step-by-step using bullet points:
To make your React Native app responsive, you need to design layouts that adapt to different screen sizes, orientations, and device types. This involves using flexible units like percentages and responsive components rather than fixed pixel values. The goal is to create a consistent user experience, whether the app is viewed on a small phone or a large tablet.
Start by using Dimensions and the useWindowDimensions hook from React Native to detect the screen size and apply conditional styles. You can also use Flexbox, which is React Native's default layout model, to create adaptable UI elements that shift and resize based on screen width or height.
For more advanced control, libraries like React Native Responsive UI, React Native Responsive FontSize, or NativeWind (Tailwind CSS for React Native) help scale text, spacing, and layout components proportionally.
Testing on multiple screen resolutions and using tools like Expo's device preview or Android/iOS emulators ensures your UI remains balanced and user-friendly across all devices.
It takes 3 to 6 months to develop a React Native app, with timelines varying based on app scope, team size, and platform-specific requirements. A basic app with 4–5 screens, simple navigation, and no backend can be built in about 8 to 12 weeks.
Mid-range apps, such as e-commerce platforms or booking systems with APIs, payment integration, and real-time updates, usually require 4 to 5 months, including testing and debugging across iOS and Android.
Complex apps, such as those with offline capabilities, geolocation, custom animations, push notifications, or multi-language support, may take 6 months or more, especially if built for both platforms with separate app store deployment configurations and rigorous QA processes.
The main difference between a web app and a React Native app is that a web app runs in a browser and is built with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, while a React Native app is installed on a mobile device and uses native components rendered through JavaScript.
Web apps are accessed via URLs and rely heavily on internet connectivity, while React Native apps function more like native apps with better offline capabilities, deeper integration with device hardware, and availability through the App Store or Google Play Store.
Secondary differences include performance—React Native apps are faster and smoother because they interact directly with mobile OS features, whereas web apps are limited by browser capabilities.
React Native also supports push notifications, background tasks, and native APIs like the camera or GPS, which are either restricted or unavailable in standard web applications.
The main difference between a hybrid app and a React Native app is that a hybrid app runs inside a WebView using web technologies, while a React Native app uses JavaScript to render real native components on mobile platforms. This means React Native apps perform closer to native standards, offering better UI responsiveness and smoother animations.
Hybrid apps rely on frameworks like Ionic or Cordova, which package web content in a native shell, often resulting in slower performance and limited access to device features. In contrast, React Native apps directly use platform APIs and native modules, making them more suitable for apps that require complex gestures, offline support, and deeper hardware integration.
The main difference between a React Native app and a Progressive Web App (PWA) is that a React Native app is installed on a device and built using JavaScript with access to native components, while a PWA runs in a browser and mimics native behaviour using web technologies. React Native apps are published on the App Store or Google Play Store, whereas PWAs are accessed via a URL and installed directly from the browser.
React Native apps offer deeper integration with device hardware, such as cameras, sensors, and push notifications, and perform better due to their native rendering. PWAs are lighter, easier to update, and require no app store approval, but they lack full offline capabilities and can be restricted by browser limitations on certain platforms like iOS.
The main difference between a React Native app and a native app is that a React Native app uses JavaScript and shares code across platforms, while a native app is written in platform-specific languages like Swift for iOS or Kotlin for Android. Native apps are built specifically for one operating system, offering maximum performance and direct access to all system APIs.
React Native apps use a bridge to communicate with native modules, which may introduce slight performance limitations in complex scenarios. However, they are faster to develop for both platforms at once, making them ideal for businesses seeking efficiency without sacrificing too much in performance or UI quality.
The main difference between a native app and a cross-platform app is that a native app is built exclusively for one operating system using its official language and tools, while a cross-platform app is developed with a single codebase that runs on multiple platforms. Native apps use tools like Xcode or Android Studio, while cross-platform apps rely on frameworks such as React Native, Flutter, or Xamarin.
Native apps deliver superior performance and complete access to device features but require separate development efforts for each platform. Cross-platform apps save time and cost by sharing most of the codebase across iOS and Android, though they might encounter limitations when implementing platform-specific functionalities.
The main difference between React Native and Flutter is that React Native uses JavaScript and bridges to native components, while Flutter uses Dart and renders its own UI engine. React Native relies on native widgets for UI, whereas Flutter creates custom widgets for both Android and iOS, ensuring consistent visuals.
React Native offers a more familiar development environment for JavaScript and React developers and has a larger ecosystem. Flutter, backed by Google, delivers high-performance and customisable UIs but has a smaller plugin ecosystem and requires learning Dart, which is less widely used.
The main difference between React Native and Swift is that React Native is a cross-platform framework using JavaScript, while Swift is a native language developed by Apple for building iOS applications. React Native enables you to build apps for both iOS and Android with a single codebase, whereas Swift is used strictly for creating high-performance apps on Apple devices.
React Native is faster for multi-platform development, but require native modules for deep system integrations. Swift offers full access to all iOS features, better runtime performance, and is ideal for apps that demand maximum responsiveness, advanced animations, or use platform-specific APIs.
The main difference between React Native and Kotlin is that React Native is a cross-platform framework using JavaScript to build apps for both iOS and Android, while Kotlin is a statically typed language used primarily for native Android development. React Native enables faster development across platforms with a shared codebase, whereas Kotlin targets the Android ecosystem for high-performance, deeply integrated apps.
React Native is ideal for launching apps on multiple platforms with one team, while Kotlin provides better control, performance, and access to Android-specific features. Kotlin Multiplatform is emerging as a cross-platform solution, but it still requires more platform-specific coding compared to React Native.
The main difference between React Native and Xamarin is that React Native uses JavaScript to render native components, while Xamarin uses C# and the .NET framework to build cross-platform apps. React Native allows faster prototyping with a large ecosystem, while Xamarin offers deeper integration with platform APIs through shared C# logic.
React Native benefits from a broader open-source community and faster development cycles, whereas Xamarin is backed by Microsoft and suits developers already working within the .NET environment. Xamarin apps require more manual UI adjustments across platforms, while React Native excels in creating native-like interfaces with minimal effort.
The main difference between React Native and Ionic is that React Native renders native UI components using JavaScript, while Ionic uses web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript inside a WebView. This means React Native apps look and perform more like native apps, whereas Ionic apps rely on browser-based rendering.
React Native offers better performance and deeper access to device features, making it suitable for more complex, high-interaction apps. Ionic is easier to set up for web developers and ideal for simpler apps or prototypes, but it faces limitations in delivering a fully native experience.
To choose the right React Native app development company, look for a team with proven experience in building cross-platform apps, a strong portfolio, and expertise in tools like React Native CLI, Expo, and Firebase. A reliable company should offer clear timelines, transparent pricing, post-launch support, and client testimonials that reflect real-world app performance.
Here are tips to help you choose the right React Native app development company:
Selecting the right partner ensures your app meets business goals and delivers a top-tier user experience. For hands-on experience, end-to-end services from design to deployment, and strong client satisfaction through post-launch support and technical agility, you should consider Intelivita for React Native app development.
It costs an average of £20,000 to £90,000 to develop a React Native app in the UK, depending on the app's complexity, features, and platform requirements. A basic app with limited screens and functionality falls within the £20,000 to £35,000 range, while a mid-level app with user authentication, backend integration, and custom UI costs between £40,000 and £60,000.
Complex apps, such as on-demand platforms, social networks, or finance apps, exceed £75,000, especially when built for both iOS and Android with custom APIs, offline support, and frequent updates.
Costs are influenced by developer rates, project duration, third-party service usage, app testing depth, and ongoing maintenance needs after launch.
The best practices for React Native app development are using modular code, following platform design guidelines, optimising performance, and thoroughly testing across devices. These practices help you build apps that are easier to maintain, more responsive, and consistent across both iOS and Android environments.
The best practices for React Native app development are:
The top trends in React Native app development include performance enhancements, native integration improvements, and broader ecosystem support. Each of these trends enables developers to build better mobile experiences more quickly.
The trends in react native app development are explained below:
Yes, startups should choose React Native app development when they need to launch quickly on both iOS and Android using a shared codebase, particularly if they have limited budgets or a small development team. It's a strong fit for MVPs, ecommerce platforms, and apps focused on UI and moderate use of native features.
However, React Native is not ideal if your app requires heavy graphics processing, extensive native integrations, or highly platform-specific functionality, such as advanced camera or sensor control. In those cases, building a fully native app may provide better performance and flexibility.
Yes, React Native apps can be deployed to both the Google Play Store and the App Store. React Native compiles into native code, allowing you to package and submit your app just like any other mobile application.
You'll follow the same publishing steps, setting up app store metadata, screenshots, permissions, and signing keys, using tools like Android Studio for APK builds or Xcode for iOS packaging. Both platforms accept React Native apps, provided they meet store guidelines and performance expectations.
Yes, React Native apps work offline. You implement offline functionality using local storage solutions like AsyncStorage, Realm, or SQLite, which allow the app to store and retrieve data without internet access.
This is especially useful for apps involving note-taking, offline browsing, or data entry, where users need to interact with the app in low-connectivity environments. Developers also implement sync logic to update the backend once the connection is restored.
Sign up now and get notified when we publish a new article!
Co-Founder
Hey there. I am Dhaval Sarvaiya, one of the Founders of Intelivita. Intelivita is a mobile app development company that helps companies achieve the goal of Digital Transformation. I help Enterprises and Startups overcome their Digital Transformation and mobile app development challenges with the might of on-demand solutions powered by cutting-edge technology.