
Physical fitness is a state of health and well-being that allows individuals to perform daily activities with vigour, minimise health risks, and maintain optimal bodily function. It encompasses various aspects of health, including cardiovascular health, muscular strength, flexibility, and endurance.
Achieving physical fitness requires a consistent exercise routine, proper exercise techniques, and a commitment to a balanced lifestyle. According to a survey by the Department of Health and Social Care, in 2022-23, 67.1% of adults in England were physically active, while 22.6% were inactive.
The types of physical fitness are cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, and body composition. These categories address different aspects of health and fitness, such as improving heart function, building muscle, and enhancing mobility. Each type plays a unique role in maintaining a holistic fitness regimen and supports individuals in achieving their specific health goals, from weight management to increased athletic performance.
Physical fitness is built on five key components: cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, and body composition. These components represent measurable aspects of fitness that collectively define one's health and physical capabilities. Addressing these elements through structured exercise routines and proper techniques helps create a well-rounded fitness plan that promotes overall well-being and reduces the risk of chronic illnesses.
The benefits of regular physical activity and maintaining physical fitness include improved cardiovascular health, enhanced muscular strength, better weight management, reduced stress levels, and a boost in mental health. Regular exercise has been shown to lower the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes and hypertension by 17% and 19%, respectively, according to the World Health Organisation (WHO). Individuals enjoy a healthier, more balanced lifestyle by incorporating fitness into daily routines.
The most popular fitness apps include 8fit, Aaptiv, Apple Fitness+, Blogilates, and FitOn. Each provides a range of services, including personalised fitness plans, guided workouts, and progress tracking. These apps make fitness accessible and enjoyable, offering features that cater to various fitness levels and preferences. With the help of these innovative tools, maintaining an effective exercise routine and tracking progress has become more convenient than ever.
What is Physical Fitness?
Physical fitness is the overall state of an individual's physical health, achieved through regular exercise and healthy habits. It includes various aspects such as cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength, flexibility, and body composition.

Good physical fitness is characterised by the body's ability to perform daily tasks efficiently without undue fatigue or risk of injury. Exercise is important in improving and sustaining physical fitness by improving the body's strength, stamina, and flexibility, eventually contributing to a healthier, more active lifestyle.
What are the Facts About Physical Fitness?
The facts about physical fitness include improved cardiovascular health, enhanced mental well-being, better weight management, and stronger immunity, all of which contribute to overall health and well-being. These facts highlight the importance of exercise, its role in various bodily functions, and the benefits of maintaining good physical fitness.

The facts about physical fitness are as follows:
- Regular exercise improves cardiovascular health: Regular physical activity strengthens the heart, reduces blood pressure, and improves circulation. This helps prevent cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes and improves the heart's ability to pump blood effectively, ensuring better oxygen and nutrient delivery throughout the body.
- Exercise boosts mental health: Physical activity releases endorphins, a natural mood enhancer. Exercise helps reduce anxiety, depression, and stress while improving cognitive function, memory, and overall emotional well-being. Regular physical activity is also linked to better sleep, further improving mental health.
- Physical fitness supports weight management: Physical activity maintains a physically fit body and helps regulate weight by balancing energy intake and expenditure. Regular exercise and a healthy diet increase metabolism and reduce body fat while promoting lean muscle mass. Physical activity also helps prevent obesity and associated health problems like diabetes and joint issues.
- Exercise improves flexibility and mobility: Consistent physical activity improves flexibility by stretching muscles and increasing joint mobility. It prevents injuries by enhancing the range of motion in muscles and joints, making it easier to perform daily tasks and activities without strain or discomfort.
- Physical fitness strengthens the immune system: Regular exercise improves immune function by promoting immune cell circulation throughout the body. It helps reduce the risk of infections, boost the body's response to illnesses, and encourage quicker recovery. Overtraining has the opposite effect, so a balanced approach to physical fitness is key.
- Exercise contributes to longevity: Regular physical fitness activities are associated with a longer lifespan. Exercise helps reduce the risk of chronic diseases, enhances mental health, and maintains functional ability into old age. A study by Bélanger A, Martel L, Berthelot JM, Wilkins R. et al., 2002, titled “Gender differences in disability-free life expectancy for selected risk factors and chronic conditions in Canada,” shows that physically active individuals tend to live longer than sedentary individuals, with an estimated additional 6.9 years of life.
What are the Types of Physical Fitness?
The different types of physical fitness are cardiovascular training, high-intensity interval training (HIIT), strength training, yoga, pilates, callisthenics, powerlifting, cycling, and martial arts. These different types of fitness focus on various aspects of physical health, from endurance to strength to flexibility.
The types of physical fitness are as follows:
Cardiovascular Training
Cardiovascular training, also known as aerobic exercise, is designed to improve the heart, lungs, and circulatory system efficiency. Activities like running, swimming, cycling, or walking elevate the heart rate for sustained periods, which boosts oxygen delivery to muscles and organs. This leads to increased endurance and cardiovascular health.
Cardiovascular exercise is performed at moderate intensity for a minimum of 20-30 minutes per session several times a week. It is done to improve overall heart health, increase stamina, and burn fat. It is ideal for anyone looking to reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and obesity.
Cardiovascular training is accessible to almost all fitness levels, but those with severe heart conditions or joint issues should consult a medical professional before beginning intensive aerobic activity. Benefits of this physical fitness type include improved heart function, decreased blood pressure, better respiratory efficiency, increased caloric expenditure, and overall enhanced energy levels.
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) alternates short bursts of intense activity with brief periods of rest or low-intensity exercise. HIIT include exercises like sprinting, jumping jacks, or burpees and lasts for 15-30 minutes.
The goal is to push the body to its maximum capacity during high-intensity phases, followed by quick recovery intervals. HIIT is extremely effective for burning fat, improving cardiovascular health, and increasing metabolic rate. It is particularly useful for those with time constraints since it provides significant benefits in a shorter duration compared to traditional cardio exercises.
While HIIT is adapted to fit various fitness levels, individuals with heart conditions, joint issues, or severe obesity should approach it cautiously or consult a healthcare provider before starting.
The benefits of HIIT include fat loss, improved cardiovascular fitness, increased muscle endurance, and higher metabolism even after the workout has ended due to the afterburn effect (excess post-exercise oxygen consumption or EPOC).
Strength Training
Strength training, or resistance training, involves activities that challenge the muscles through weights, bodyweight exercises, or resistance bands. Common examples of resistance training include squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and push-ups. This type of training focuses on building muscle mass, improving strength, and increasing endurance.
Strength training is performed by gradually increasing the weight or resistance to enhance the muscles' ability to lift or push against external forces. The primary goal is to build muscle tissue, improve bone density, and boost metabolic rate.
Resistance training benefits anyone looking to increase muscle size, improve functionality, or prevent muscle loss due to ageing. Those with osteoporosis, arthritis, or heart conditions should take precautions and consider lighter weights with proper technique.
Yoga
Yoga is a holistic practice combining physical postures (asanas), controlled breathing (pranayama), and meditation. It is performed to improve flexibility, strength, balance, and mental clarity. Yoga is done on a mat, using only the body, or with props like blocks or straps for added support.
There are many styles of yoga, ranging from gentle practices like Hatha yoga to more dynamic forms like Vinyasa or Ashtanga. Yoga is performed in a calm environment, emphasising mindfulness and breath control. It is done to increase flexibility, reduce stress, and enhance mental focus.
Yoga is suitable for all fitness levels and ages, but individuals with severe flexibility limitations or joint injuries should choose restorative or gentle forms of yoga. Benefits of yoga include improved posture, reduced anxiety, better balance and coordination, increased joint mobility, and enhanced mental calmness and clarity.
Pilates
Pilates is a low-impact exercise system focused on strengthening the core, improving flexibility, and promoting body alignment. It involves controlled movements and breathing techniques aimed at enhancing posture and balance.
Pilates exercises are performed on a mat or using specialised equipment like a reformer. They improve core stability, increase muscle endurance, and prevent injury. Pilates is ideal for individuals of all fitness levels, especially those recovering from injury or chronic pain, as it emphasises controlled and precise movements.
Pilates improves posture, reduces back pain, increases abdominal strength, and enhances overall flexibility. However, those with severe orthopaedic issues should seek professional guidance before starting Pilates.
Callisthenics
Callisthenics refers to bodyweight exercises such as push-ups, pull-ups, squats, lunges, and dips, performed without external equipment. These exercises are designed to build strength, flexibility, and endurance by using the body's own weight as resistance.
Callisthenics is a highly versatile workout method that focuses on form and controlled movement. It requires minimal equipment and is done in sets and repetitions, making it accessible for home workouts or outdoor training. Calisthenics improves functional strength, body control, and overall fitness.
While individuals of all fitness levels perform callisthenics, beginners should start with modified exercises until they build strength. The benefits of callisthenics include improved muscle endurance, better coordination, enhanced flexibility, and increased strength without the need for expensive gym equipment.
Powerlifting
Powerlifting is a strength training discipline focused on maximal strength in three major lifts: the squat, deadlift, and bench press. The primary goal of powerlifting is to increase the maximum weight an individual lifts in these movements. Powerlifters follow a structured program that emphasises progressive overload, meaning they gradually increase the weight lifted over time.
Individuals looking to maximise strength and muscle mass prefer powerlifting over other forms of physical fitness. Powerlifting is not recommended for beginners without prior strength training experience, as lifting maximum weights is risky without proper technique.
Powerlifting helps increase muscle mass, strength, and bone density, as well as develop functional power for other sports or activities.
Cycling
Cycling, whether on a stationary bike or outdoors, is a cardiovascular exercise that strengthens the heart, tones leg muscles and improves endurance. Cycling is performed for extended periods at moderate intensity, either in structured sessions or as part of a recreational activity.
This type of physical exercise is beneficial for improving cardiovascular health, building leg strength, and enhancing stamina. Cycling is a low-impact exercise, making it accessible for people of various fitness levels, especially those with joint issues or injuries. Individuals with severe knee or hip problems should consult a healthcare provider before starting regular cycling.
Cycling is recommended for patients with a risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes as it improves cardiovascular function and helps with weight management. Cycling also increases leg muscle strength and enhances endurance.
Martial Arts
Martial arts encompass a wide range of combat disciplines, including karate, taekwondo, judo, Brazilian jiu-jitsu, and boxing. These practices combine physical conditioning with self-defence techniques, focusing on strength, agility, flexibility, and mental discipline.
Martial arts training includes intense drills, sparring, and kata (forms), which are performed to improve coordination, reflexes, and mental focus. It is practised by individuals looking for physical and mental challenges, providing a full-body workout.
For anyone wanting to develop discipline, self-defence skills, and improve endurance, martial arts is the best physical fitness. However, martial arts is not suitable for individuals with certain physical limitations or those who are not comfortable with physical contact, depending on the discipline.
What are the Components of Physical Fitness?
The key components of physical fitness include cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, and body composition. These components work together to improve overall physical health and develop a balanced and functional body.
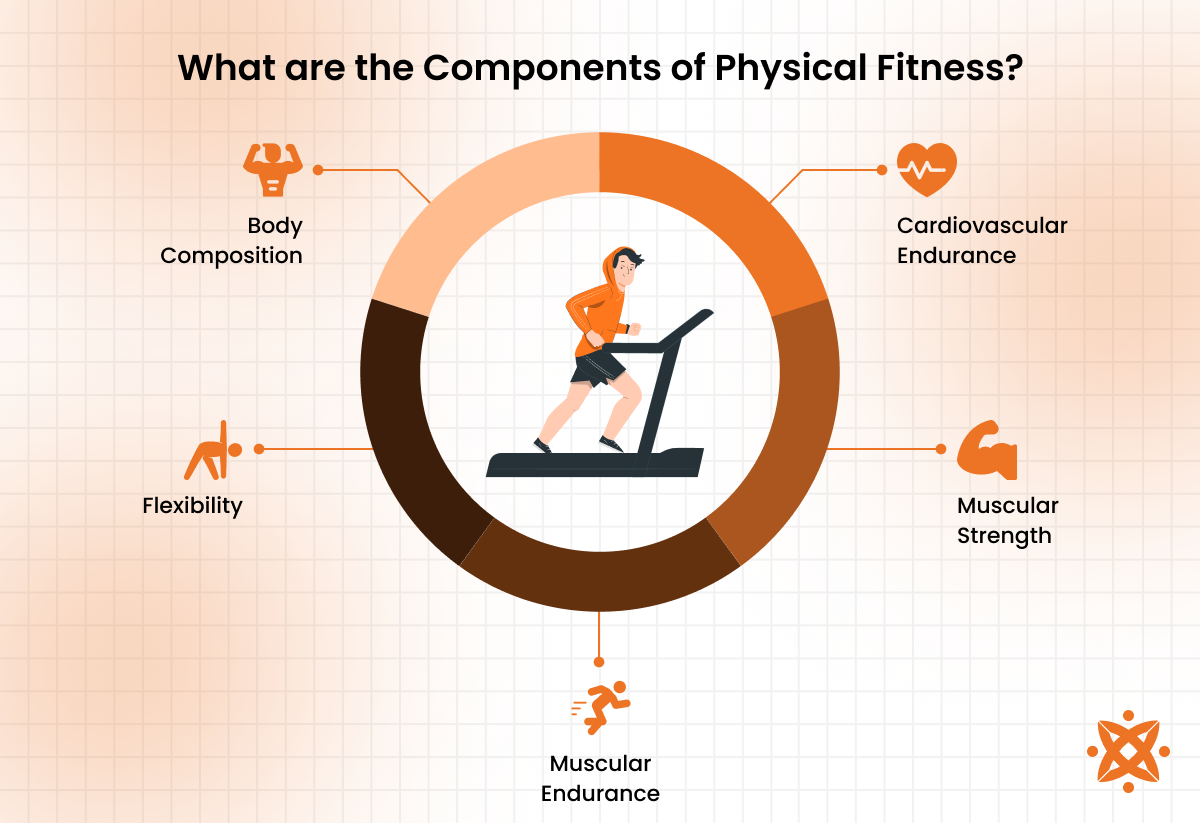
The key components of physical fitness are as follows:
- Cardiovascular Endurance: Cardiovascular endurance refers to the ability of the heart, lungs, and blood vessels to supply oxygen and nutrients to the muscles during prolonged physical activity. This component is important for activities such as running, swimming, and cycling. Good cardiovascular endurance improves heart efficiency, lowers the risk of heart disease, and enhances overall stamina. It enables individuals to perform longer and more intense physical tasks without exhaustion, and it has been shown to improve longevity and reduce the risk of chronic diseases like hypertension, stroke, and diabetes.
- Muscular Strength: Muscular strength is the maximum amount of force a muscle or group of muscles generates. It is developed through exercises like weight lifting, squats, and resistance training. Strong muscles improve overall body function, improve posture, and allow for the performance of physical tasks with greater ease and power. Muscular strength is important for daily activities such as lifting, pushing, and carrying, and preventing injuries by providing support and stability to joints. Muscular strength helps boost metabolism and contributes to greater bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis, according to the Mayo Clinic.
- Muscular Endurance: Muscular endurance refers to the ability of a muscle to sustain repeated contractions over time without fatigue. This component is important for activities like cycling, rowing, and long-distance running. Muscular endurance enriches stamina and performance in prolonged physical tasks, making it important for athletes, manual labourers, and anyone engaging in repetitive physical movements. A scientific study by Sundstrup E et al. 2016, titled “Strength Training Improves Fatigue Resistance and Self-Rated Health in Workers with Chronic Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial”, show that improving muscular endurance reduces the likelihood of muscle fatigue and injury while also improving recovery time after exertion. It is particularly beneficial for maintaining good posture and supporting endurance activities like climbing, swimming, and hiking.
- Flexibility: Flexibility is the range of motion available in a joint or series of joints. This component is necessary for maintaining mobility, preventing injuries, and improving posture. Flexibility is developed through activities such as yoga, Pilates, and dynamic stretching. Increased flexibility allows for better movement efficiency, reduces muscle tension, and minimises the risk of strains and sprains. Scientifically, flexibility improves muscle elasticity and joint lubrication, paramount for maintaining joint health, particularly at one age. It also aids recovery following intense physical activity and enhances athletic performance by improving balance and coordination.
- Body Composition: Body composition refers to the proportion of body fat and lean mass (muscle, bone, and organs). A healthy body composition is characterised by a lower percentage of body fat and a higher proportion of lean muscle mass. Maintaining an optimal body composition is important for overall health, as excessive body fat is linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and joint problems. A higher muscle mass improves metabolic rate, allowing the body to burn more calories at rest while reducing fat stores. Achieving a balanced body composition through a combination of cardiovascular exercise, strength training, and healthy eating is necessary for improving both physical appearance and health outcomes.
What are the Benefits of Physical Fitness?
The main benefits of physical fitness are improved cardiovascular health, enhanced mental well-being, better weight management, increased strength and endurance, and a reduced risk of chronic diseases. These benefits contribute to overall health and longevity, improving both physical and mental quality of life.
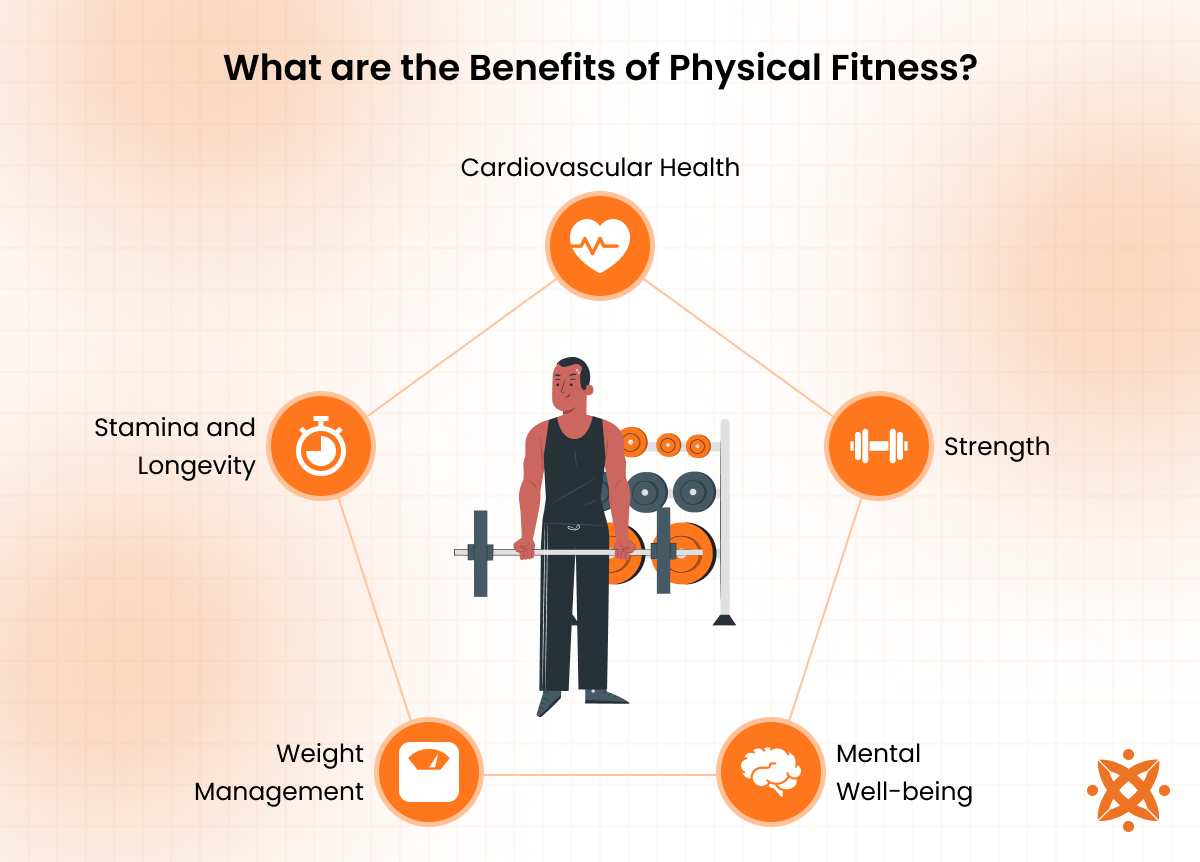
The main benefits of physical fitness are as follows:
- Improved Cardiovascular Health: Regular physical fitness activities such as running, swimming, or cycling significantly improve heart health by increasing cardiovascular endurance and reducing blood pressure. Individuals who engage in regular exercise have a lower risk of heart disease, stroke, and high cholesterol. The American Heart Association suggests at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic weekly exercise to maintain heart health. Physical fitness strengthens the heart muscle, improves blood circulation, and enhances oxygen delivery to tissues, which leads to a lower resting heart rate and reduced risk of cardiovascular issues.
- Enhanced Mental Well-Being: Physical fitness has a profound positive impact on mental health by reducing symptoms of anxiety, depression, and stress. Exercise triggers the release of endorphins, which are known as "feel-good" hormones that improve mood and reduce feelings of depression. Research by Craft LL, Perna FM. et al. 2004, titled “The Benefits of Exercise for the Clinically Depressed”, indicates that regular physical activity is as effective as antidepressant medications in treating mild to moderate depression, and it is known to reduce anxiety levels and improve sleep quality. Physical activity boosts cognitive function, memory, and focus, improving mental clarity and overall emotional well-being, as studied by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- Better Weight Management: Engaging in regular physical activity helps regulate weight by increasing the number of calories burned. A study by Khalafi M et al. 2023, titled “ The effects of exercise training on body composition in postmenopausal women: a systematic review and meta-analysis”, shows that combining aerobic exercise with strength training is particularly effective for fat loss and improving body composition. Regular exercise boosts metabolism and increases lean muscle mass, further accelerating fat burning, even at rest. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week to maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of obesity-related diseases such as type 2 diabetes and hypertension.
- Increased Strength and Endurance: Strength training and endurance exercises significantly increase muscle mass, bone density, and overall strength. Regular strength training improves muscle function, enhances joint stability, and reduces the risk of falls, especially in older adults. A large research study by Sherrington C et al. 2019, titled “Exercise for preventing falls in Older People Living in the Community”, analysed nearly 8,000 older adults and found that balance and functional exercises reduce the rate of falls by 24%. Endurance training, on the other hand, boosts stamina, allowing individuals to perform physical tasks over longer periods without fatigue. It also improves overall body performance, making daily activities easier, such as carrying groceries or climbing stairs.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: Regular physical fitness activities lower the risk of developing chronic health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, obesity, certain cancers, and osteoporosis. According to a study by Warburton DE, Nicol CW, Bredin SS. et al. 2006, titled “Health benefits of physical activity: the evidence”, physically active individuals have a lower incidence of these conditions compared to those who are sedentary. Regular exercise helps regulate blood sugar levels, lowers inflammation, and improves insulin sensitivity, significantly reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes. Physical fitness also maintains bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures as individuals age.
What are the Challenges of Physical Fitness?
The main challenges of physical fitness are maintaining consistency, overcoming lack of motivation, finding time, dealing with physical limitations, and managing unrealistic expectations. These challenges hinder individuals from achieving their fitness goals and require strategies to address them effectively.
The challenges of physical fitness are as follows:
- Maintaining Consistency: One of the most significant physical fitness challenges is staying consistent with a workout routine. Many people start with enthusiasm but lose momentum due to busy schedules, lack of results, or boredom. It takes around 21 days to build a habit, but staying consistent requires long-term planning and commitment. Consistency is important for achieving fitness goals, as sporadic efforts do not yield significant results.
- Overcoming Lack of Motivation: Motivation fluctuates, making it challenging to stick to a fitness regimen. External factors like stress, fatigue, or lack of visible progress discourage individuals. Setting realistic goals, tracking progress, and finding enjoyable activities help maintain motivation. Support from friends, family, or a fitness coach sustains enthusiasm.
- Finding Time: Balancing work, family, and other commitments leaves little time for exercise. Lack of time is one of the most commonly cited reasons for not staying active. Including short, high-impact workouts like High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) or combining activities with daily tasks, such as cycling to work, help overcome this challenge. Time management and prioritising health are important for making fitness a consistent part of life.
- Dealing with Physical Limitations: Physical injuries, chronic conditions, or age-related issues also limit the type or intensity of exercises an individual performs. These limitations lead to frustration or avoidance of physical activity altogether. Customised exercise plans designed by healthcare professionals or fitness experts help individuals stay active within their abilities. Even low-impact exercises like yoga or walking significantly benefit overall health if done consistently.
- Managing Unrealistic Expectations: Many people expect immediate results from their fitness efforts, leading to disappointment and discouragement when progress is slower than anticipated. Unrealistic expectations result from misinformation or comparing oneself to others. Fitness improvements, such as weight loss or muscle gain, require patience and long-term commitment. Setting achievable milestones and focusing on long-term benefits rather than short-term changes help manage expectations.
What are the Common Physical Fitness Apps?
The common physical fitness apps include 8fit, Aaptiv, Apple Fitness+, Blogilates, FitOn, MyFitnessPal, Nike Training Club, and Strava. These apps offer diverse features, from guided workouts and progress tracking to personalised fitness plans, catering to users with varying fitness goals and levels of expertise. These fitness apps make wellness accessible and convenient, allowing users to stay active anytime, anywhere.

The common physical fitness apps are as follows:
- 8fit: 8fit combines fitness and nutrition guidance, offering personalised workout plans and healthy meal suggestions. It focuses on helping users achieve fitness goals like weight loss or muscle gain through a combination of exercise routines and dietary advice. The app's step-by-step approach makes it ideal for beginners and those seeking structured guidance.
- Aaptiv: Aaptiv provides audio-based workouts led by professional trainers. It covers a variety of fitness categories, including running, strength training, and yoga. The app's flexibility and motivational audio cues make it an excellent choice for users who prefer guided sessions without constantly looking at a screen.
- Apple Fitness+: Apple Fitness+ integrates seamlessly with Apple devices, offering diverse workout types like HIIT, cycling, and yoga. The app provides real-time metrics on the screen, such as heart rate and burned calories, making it highly interactive and engaging for Apple users.
- Blogilates: Blogilates is designed for fans of Pilates and bodyweight workouts, featuring routines led by fitness influencer Cassey Ho. The app offers a mix of free and premium content, including workout calendars and challenges that are perfect for users seeking a community-driven fitness journey.
- FitOn: FitOn offers free workouts across various categories, such as cardio, strength, and mindfulness. It also features celebrity trainers, making the workouts fun and motivating. The app's accessibility and variety make it suitable for users of all fitness levels.
- MyFitnessPal: MyFitnessPal is a comprehensive fitness app emphasising calorie tracking and nutritional awareness. It includes a vast food database and integrates with other fitness devices to track workouts, providing a holistic approach to fitness and health management.
- Nike Training Club: Nike Training Club offers expertly designed workouts ranging from beginner to advanced levels. The app features strength training, yoga, and endurance sessions, along with tips from professional trainers. It's ideal for users seeking structured programs to build fitness and strength.
- Strava: Strava is a favourite among runners and cyclists, offering route tracking, performance analytics, and social networking. The app's community features encourage friendly competition and motivation, making it a go-to for endurance athletes and outdoor enthusiasts.
What are the Features of a Fitness App?
The features of a fitness app are workout tracking, personalised fitness plans, nutritional guidance, progress monitoring, integration with wearable devices, community engagement, and virtual coaching. These features enhance user experience, making fitness accessible, enjoyable, and customised to individual needs.
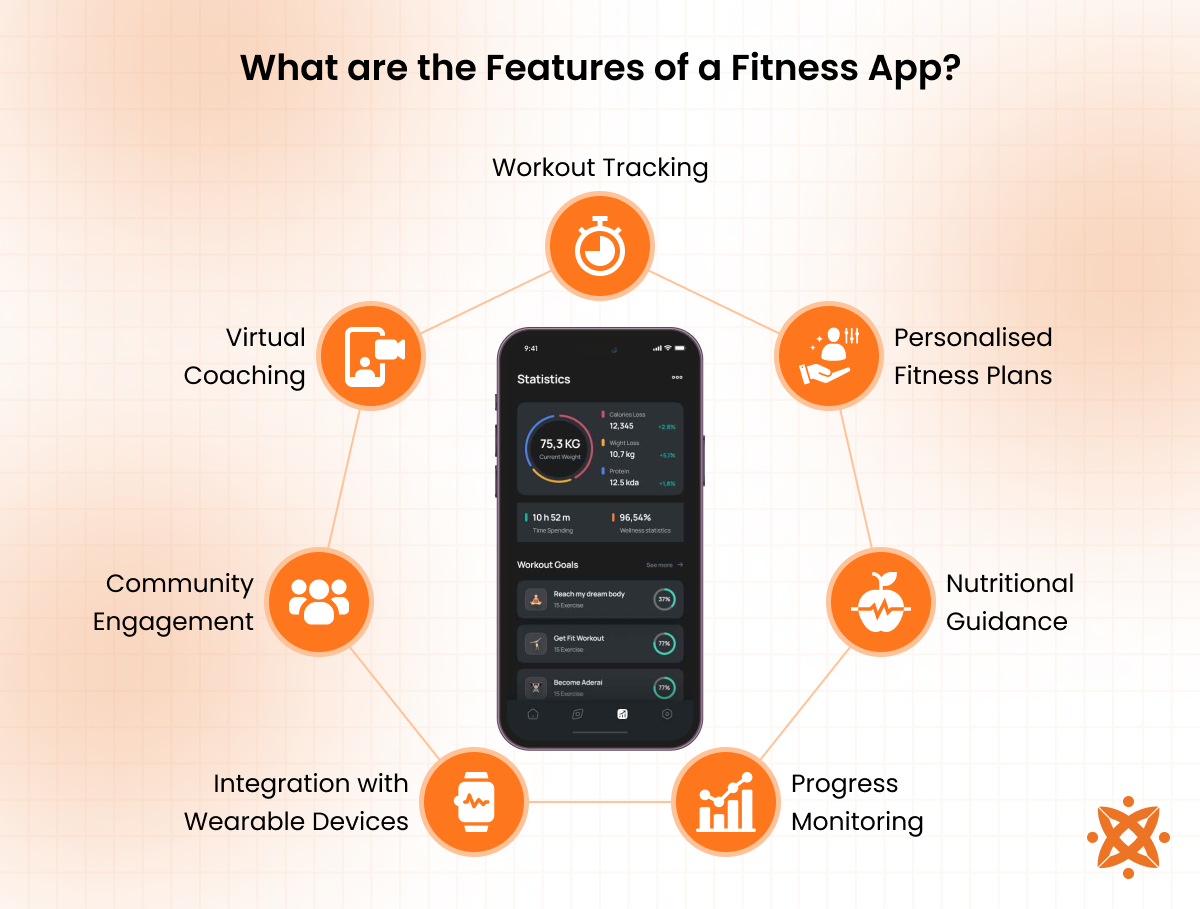
The features of a fitness app are as follows:
- Workout Tracking: Fitness apps allow users to log and track their workouts, including exercise type, duration, and intensity. This feature helps users monitor progress, identify patterns, and stay consistent in their fitness routines. By providing insights into performance, workout tracking encourages users to stay motivated and achieve their fitness goals.
- Personalised Fitness Plans: Many fitness apps create custom workout plans based on the user's fitness level, goals, and preferences. This feature ensures that users engage in exercises that are personalised to their needs, whether they aim to lose weight, build muscle, or improve endurance. Personalised plans offer structure, making fitness journeys more efficient and results-oriented.
- Nutritional Guidance: Most apps include a nutritional component, such as meal planning, calorie tracking, or healthy recipe suggestions. This feature complements physical activity by helping users maintain a balanced diet that supports their fitness goals. Proper nutrition is key to achieving long-term health and fitness outcomes.
- Progress Monitoring: Progress monitoring tools track metrics like weight changes, calorie expenditure, and workout performance over time. These features provide users with a clear picture of their achievements and areas for improvement. Visual representations, such as charts or graphs, make it easier for users to stay motivated and adapt their routines as needed.
- Integration with Wearable Devices: Fitness apps integrate with wearable devices like smartwatches or fitness trackers, syncing data such as heart rate, steps, and sleep patterns. This connection enhances user experience by providing comprehensive health insights and enabling real-time tracking during workouts.
- Community Engagement: Social features, such as challenges, leaderboards, and group forums, promote a sense of community among users. Engaging with others through the app increases accountability, motivation, and enjoyment. Many apps also allow users to share achievements, creating a supportive environment for reaching fitness goals.
- Virtual Coaching: Virtual coaching offers guided workouts led by professional trainers through video or audio instructions. This feature ensures proper technique and offers motivation, making it feel like users have a personal trainer at their convenience. It's particularly beneficial for beginners who need step-by-step guidance.
What is the Difference Between Physical Fitness and Mental Fitness?
The main difference between physical fitness and mental fitness is their focus. Physical fitness pertains to the health and performance of the body, while mental fitness involves the cognitive and emotional well-being of the mind.
Physical fitness is achieved through activities like exercise, which improves cardiovascular health, strength, and endurance. In contrast, mental wellness is cultivated through practices such as meditation, mindfulness, and stress management techniques, which improve focus, resilience, and emotional regulation.
Both forms of fitness are interconnected, as regular physical activity boosts mental health by releasing endorphins and reducing stress. Similarly, a mentally fit individual is more likely to maintain physical health by staying motivated and consistent in their fitness routines.
What is the Difference Between Physical Fitness and Physical Activity?
The main difference between physical fitness and physical activity is that physical activity refers to any bodily movement produced by muscles that require energy expenditure, while physical fitness is a measurable state of health and capability achieved through regular physical activity. Physical activity includes walking, gardening, or playing sports, while attributes like strength, endurance, flexibility, and cardiovascular health characterise physical fitness.
Physical fitness is a goal or outcome of consistent physical activity. For instance, regular running (a physical activity) improves cardiovascular endurance (a component of physical fitness). While physical activity encompasses all forms of movement, physical fitness reflects the effectiveness and efficiency of how well the body performs these movements.
What is the Difference Between Physical Fitness and Biological Fitness?
The main difference between physical fitness and biological fitness is their context. Physical fitness refers to an individual's ability to perform physical tasks efficiently, while biological fitness pertains to an organism's ability to survive and reproduce in its environment.
Although the terms share the word "fitness," their meanings and applications differ significantly. Physical fitness is associated with health and exercise, involving components like strength, endurance, and flexibility. In contrast, biological fitness is a concept in evolutionary biology that measures the success of an organism in passing its genes to the next generation.
For example, a person who exercises regularly exhibits physical fitness, while an organism that adapts effectively to its environment and reproduces successfully demonstrates biological fitness.
Never Miss an Update From Us!
Sign up now and get notified when we publish a new article!
Oliver Baker
Co-Founder
Oliver Baker is a co-founder of Intelivita, a leading Web and Mobile App Development Company based in Leeds, UK. Oliver has been at the forefront of the business, expanding it globally and into new technologies including iOS and Android, AR, VR and Mobile Game applications. Oliver excels in Project Management, Leadership, Quality Assurance and Problem Solving and has qualifications with Prince2 and APM. He aims to develop his skills further through a shared interest with other leaders in the Software Markets and the Clients of Intelivita.
