
A website is an important tool for sharing information, facilitating interaction, and providing functionality in the digital era, designed to address the diverse needs of users and businesses. At the core of website design and development is creating a user-friendly and accessible interface that delivers messages effectively. Websites are used for e-commerce, education, and entertainment, driving engagement through responsive web design and optimised user experiences.
According to Siteefy, there are over 1.1 billion websites globally as of 2025, but only 17% are actively maintained, with 83% inactive. Around 63% of the global population uses the internet, with mobile traffic accounting for more than half of all web usage, emphasising the importance of responsive web design. WordPress powers 43% of websites worldwide, while static websites comprise 15-20%. Over 70% of small businesses maintain a website to reach customers, and e-commerce platforms like Amazon and Alibaba dominate online retail.
Websites come in various types, from static websites that deliver fixed content to dynamic and interactive web applications. The choice depends on business goals and user demands. WordPress websites dominate for ease of use, portfolio websites cater to showcasing talent, and sticky websites focus on user retention. Mobile-friendly and SEO-optimised sites improve visibility and accessibility, making them paramount today.
The major components of a website include the domain name, web hosting, content, user interface, and backend functionality. Collectively, these elements ensure that websites are visually appealing, functional, and optimised for performance. Responsive web design and SEO integration are significant in reaching diverse audiences and boosting search engine rankings.
Building a web application involves strategic planning, including defining goals, designing intuitive user interfaces, and selecting the right technology stack. The development process integrates front—and backend functionality to create a scalable, mobile-friendly app. Testing and deploying the app with tools like AWS or Heroku ensures a polished product that meets user needs while maintaining strong performance and security.
Converting a website into a progressive web app (PWA) improves its functionality with features like offline access, faster loading, and app-like usability. The process involves enabling HTTPS, creating a web app manifest, and implementing a service worker to improve responsiveness and caching. PWAs bridge the gap between traditional websites and mobile apps by optimising performance and delivering an impressive experience.
What is a Website?
A website is a collection of interlinked web pages hosted on a specific domain and accessible via the internet. It is created using web technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript and is housed on a server. Websites range from simple static pages to complex, interactive applications. Each website has a unique URL (Uniform Resource Locator) that allows users to access its content through a web browser.

Websites serve various purposes, including sharing information, providing entertainment, facilitating communication, conducting business, and offering services. Individuals, businesses, organisations, and governments use them to disseminate content, sell products, provide support, and build communities. They also serve as tools for education, collaboration, and activism, making them versatile platforms in the digital world.
The benefits of websites include a global reach, allowing users to connect with audiences worldwide. They enable businesses to establish an online presence, which is significant for brand visibility and customer engagement. Compared to traditional advertising, websites are cost-effective as they are available 24/7 and ensure continuous access to information and services. Websites are also customised and scaled according to users' needs, making them adaptable tools for various purposes.
The website concept began with Tim Berners-Lee's creation of the World Wide Web at CERN in 1989. The first website, info.cern.ch, was launched in 1991 as a basic directory of the web's capabilities. During the 1990s, websites evolved from simple, text-based pages to more visually rich designs with the advent of web browsers like Mosaic and Netscape. The early 2000s saw the rise of dynamic websites, e-commerce, and social networking platforms.
According to Siteefy, there were over 1.1 billion websites globally as of 2025, though only a fraction are actively maintained. Only about 200 million, or 17%, are active, and 83% are inactive. Approximately 63% of the global population are internet users, accessing sites for various purposes such as shopping, learning, and entertainment.
E-commerce websites like Amazon and Alibaba dominate online retail, while platforms like Google and YouTube receive billions of daily visits. Mobile traffic accounts for more than half of internet traffic, emphasising the importance of responsive web design. Websites are important for small businesses, and over 70% of small businesses worldwide maintain a website to reach customers and grow their brands.
What are the Types of Websites?
The different types of websites are web applications, static websites, WordPress websites, portfolio websites, dynamic websites, and sticky websites. Each type serves distinct purposes, utilises specific technologies, and is suited for varying business or personal needs.
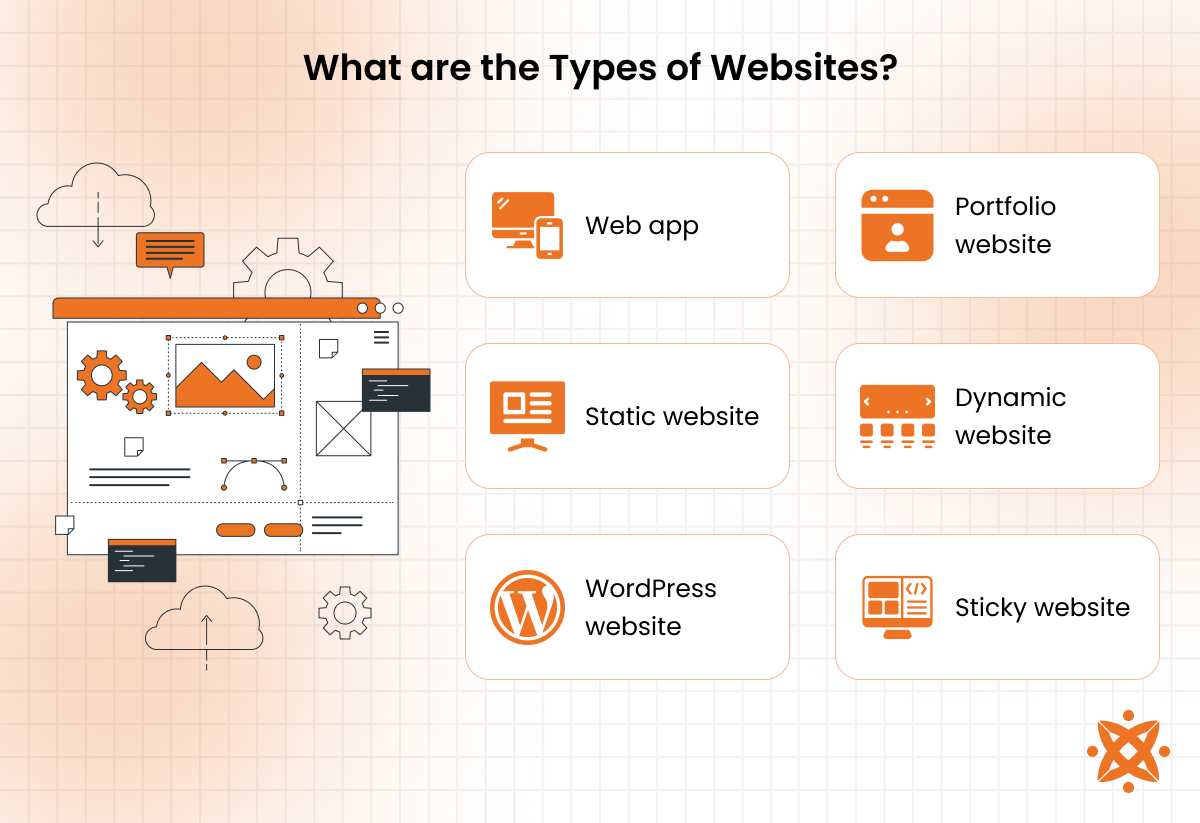
The different types of websites are as follows:
- Web app
- Static website
- WordPress website
- Portfolio website
- Dynamic website
- Sticky website
Web App
A web application is an interactive website designed to perform specific tasks or services through user interaction. Unlike static sites, web apps are highly dynamic and rely on server-side programming (e.g., PHP, Python) and client-side scripting (e.g., JavaScript) like Gmail, Facebook, and Trello.
There are millions of web applications worldwide, and industries are increasingly adopting them for e-commerce, project management, and online education. In 2024, according to Backlinko, Instagram was the most downloaded app worldwide, with 182.8 million downloads across Google Play and the App Store. It was followed by Facebook, TikTok, and WhatsApp.
The most significant benefits of web apps include accessibility to any device with an internet connection, real-time data processing, and real-time updates. Businesses such as SaaS providers, e-commerce platforms, and collaborative tools choose web apps for their functionality and scalability.
Static Website
A static website consists of fixed web pages coded in HTML and CSS. It displays the same content to all users without server-side interaction. It is simple, fast, and cost-effective, making it ideal for small businesses or informational sites.
Static websites make up about 15-20% of all websites. They are easy to create and maintain for those with limited technical resources. Their benefits include fast load times, enhanced security, and low hosting costs. They are used for portfolios, brochures, and small business sites with limited content updates.
WordPress Website
A WordPress website is built on the WordPress content management system (CMS), which powers over 43% of all websites worldwide. It is versatile and user-friendly, allowing individuals and businesses to create blogs, e-commerce sites, and corporate platforms without extensive coding knowledge.
WordPress websites benefit from thousands of themes and plugins, enabling customisation and scalability. They are used for blogging, online stores, and nonprofit websites, making them a popular choice for organisations of all sizes due to their ease of use and extensive community support.
Portfolio Website
Portfolio websites are designed to showcase creative work, skills, or achievements. They are used by professionals such as designers, photographers, and writers. These websites focus on visual appeal and user experience, and examples include Behance portfolios or personal artist sites.
They are particularly popular among freelancers and creative professionals, as they act as an online resume or gallery to attract clients. Depending on user preference, static designs are simple or dynamic, while dynamic designs are interactive.
Dynamic Website
Dynamic websites deliver tailored content to users by interacting with databases and employing server-side technologies. E-commerce sites like Amazon, where content such as product recommendations changes based on user behaviour.
Dynamic websites account for a significant majority of websites today. They offer personalisation, interactivity, and scalability. They are widely used in retail, entertainment, and education industries to enhance user engagement and meet diverse needs.
Dynamic websites achieve better performance, loading a page in as little as 3 seconds, by effectively using efficient database queries, caching mechanisms, and content delivery networks (CDNs) and quickly delivering personalised and interactive content.
Sticky Website
Sticky websites are designed to retain and keep users engaged for longer periods through compelling content, interactive features, and intuitive navigation. These websites employ gamification, engaging visuals, or continuous updates to maintain user interest.
Sticky websites are particularly beneficial for news platforms, gaming sites, and social media, where user retention drives success. Their ability to foster loyalty and promote frequent visits makes them a cornerstone of many successful online strategies.
What are the Components of a Website?
The major components of a website are the domain name, web hosting, content, user interface (UI), and backend functionality. Each element ensures that the website operates effectively and meets its purpose.
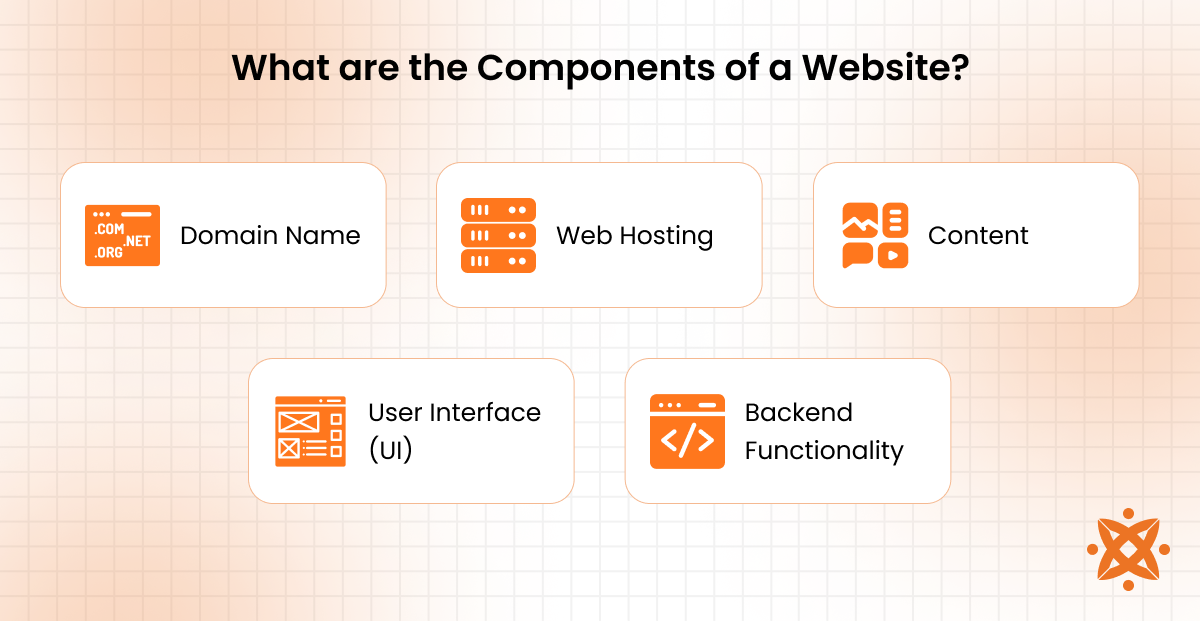
The major components of a website are as follows:
- Domain Name: The domain name is the unique address of a website, such as example.com, that users enter in their browsers to access. It represents the website's identity and is important for branding and recognition. A well-chosen domain name is memorable, aligns with the site's purpose, and helps improve its visibility in search engines.
- Web Hosting: Web hosting provides the server space where a website's files, data, and content are stored and delivered to users. Hosting ensures the site is accessible 24/7, with varying options like shared hosting, VPS, or dedicated servers based on the website's traffic and performance needs. Reliable hosting is required for speed, security, and uptime.
- Content: Content includes all the text, images, videos, and other media that convey information to the audience. It is the heart of a website, designed to engage users and fulfil their needs. Effective content is customised to the target audience, optimised for search engines, and updated regularly to maintain relevance.
- User Interface (UI): The user interface refers to the visual design and layout of the website, ensuring that it is intuitive, appealing, and easy to navigate. A well-designed UI uses clear menus, responsive design, and accessible features to enhance user experience and encourage engagement.
- Backend Functionality: The backend consists of the server-side infrastructure, databases, and programming logic that power the website. It ensures the proper functioning of features like user accounts, payment systems, and content management. A robust backend is necessary for security, scalability, and performance.
How to Build a Web App?
To build a web app requires defining goals, planning the design, selecting the right technologies, developing the front end and back end, and deploying the app. Each step is important in creating a functional, scalable, and user-friendly application that delivers value to its audience.
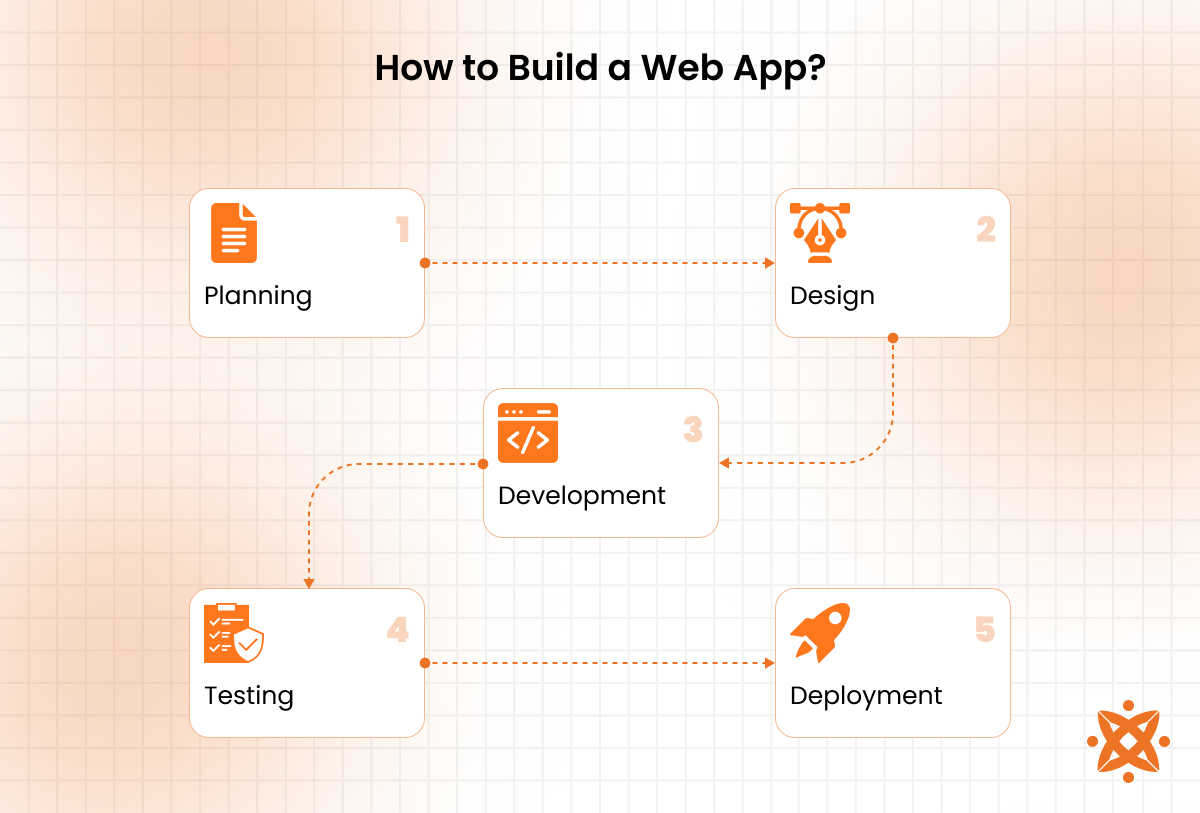
To build a web app, the following steps are used:
- Define the Purpose and Target Audience: Start by identifying your web app's purpose and the intended audience. This step helps establish goals, features, and functionality based on user needs and market demand. Conducting research and creating user personas ensures a focused and efficient development process.
- Plan and Design the App: Create a roadmap for your app, including wireframes and user interface designs. Use tools like Figma or Adobe XD to design intuitive layouts and user-friendly navigation. Planning the app's structure ensures clarity for developers and stakeholders.
- Choose the Technology Stack: The next important step is to choose an appropriate technology for the front end, back end, and database. Common choices include React or Angular for the front end, Node.js or Django for the back end, and databases like MongoDB or PostgreSQL. The stack should align with the app's requirements and scalability needs.
- Develop the front end and back end: Building the user-facing interface (front end) and server-side logic (back end) makes modern frameworks and ensures smooth interaction between components via APIs. Development should be modular and follow coding best practices to maintain quality.
- Test the Web App: Conducting thorough testing is paramount to identify and fix bugs, ensure compatibility across devices and browsers, and validate performance. Tools like Selenium or Postman assist in functional and API testing of website apps before users' feedback for further refinement.
- Deploy and Monitor: Hosting the app on a server or cloud platform and making it accessible online is the final step in website app development. Services like AWS, Azure, or Heroku for deployment help implement monitoring tools to track performance, user behaviour, and potential issues, ensuring continuous improvement.
How to Convert a Website to a Progressive Web App?
To convert a website to a progressive web app (PWA), start by enabling HTTPS for secure connections, then create a web app manifest file to define basic metadata. Next, a service worker will be implemented to provide offline functionality and caching. After optimising the website's performance, the PWA is tested thoroughly to ensure all features work error-free and offer an app-like experience for users.
To convert a website to a progressive web app, the following steps are used:
- Ensure HTTPS is Enabled: A secure connection is a fundamental requirement for PWAs. Use an SSL certificate to enable HTTPS on your website, ensuring data security and compliance with PWA standards.
- Create a Web App Manifest File: Develop a JSON file, manifest.json, that defines the app's metadata, such as its name, icons, theme colour, and start URL. This file enables the app to be installed on devices like native apps.
- Implement a Service Worker: Write and register a service worker, a script that runs in the background to manage caching, offline functionality, and push notifications. Service workers are integral in delivering a smooth, app-like experience.
- Optimise for Performance and Responsiveness: Ensure your website is mobile-friendly and loads quickly. Use tools like Google Lighthouse to audit performance and optimise images, code, and server response times. Responsiveness is key for an impactful PWA experience and a progressive website app.
- Add PWA Features and Test: Integrate additional PWA features like push notifications and installability. Test the PWA thoroughly across devices to ensure all functionalities work as expected. Use tools like Workbox for service worker management and debugging.
How to Optimize a Website for Better Performance?
To optimise a website for better performance, focus on reducing load times, improving responsiveness, and ensuring smooth functionality. Start by compressing images and minifying CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files to decrease file sizes. A Content Delivery Network (CDN) delivers resources faster to users worldwide and helps to optimise server response times by implementing caching strategies and upgrading hosting plans if necessary.
Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and Lighthouse provide detailed performance reports, enabling targeted improvements. Optimising a website's performance also requires prioritising lazy loading for images and videos, implementing responsive design, and regularly auditing third-party scripts to minimise unnecessary resource usage.
A faster website leads to better user engagement, higher search engine rankings, and increased conversions. According to HubSpot, the average website load time in 2023 is 2.5 seconds on desktop and 8.6 seconds on mobile, based on an analysis of over 4 billion web visits. Littledata's statistics show that websites must load in under 2.9 seconds to rank among the top 20% of the fastest websites, and a one-second delay in load time leads to 16% lower user satisfaction.
What are the Best Practices for Website Design and Development?
The best practices for website design and development include focusing on responsive design, optimising performance, and ensuring accessibility. A well-designed website adapts to various devices, prioritises user experience, and adheres to web standards. Using clean, semantic code and following SEO guidelines improves search engine visibility and usability.
For continuous improvement, content should be regularly updated, analytics tools integrated, and user testing conducted. Security measures, such as SSL encryption and regular updates, protect user data and build trust. Businesses create impactful websites that balance functionality, aesthetics, and performance to meet user and market needs.
Never Miss an Update From Us!
Sign up now and get notified when we publish a new article!
Oliver Baker
Co-Founder
Oliver Baker is a co-founder of Intelivita, a leading Web and Mobile App Development Company based in Leeds, UK. Oliver has been at the forefront of the business, expanding it globally and into new technologies including iOS and Android, AR, VR and Mobile Game applications. Oliver excels in Project Management, Leadership, Quality Assurance and Problem Solving and has qualifications with Prince2 and APM. He aims to develop his skills further through a shared interest with other leaders in the Software Markets and the Clients of Intelivita.
